Boiling Point Drawing
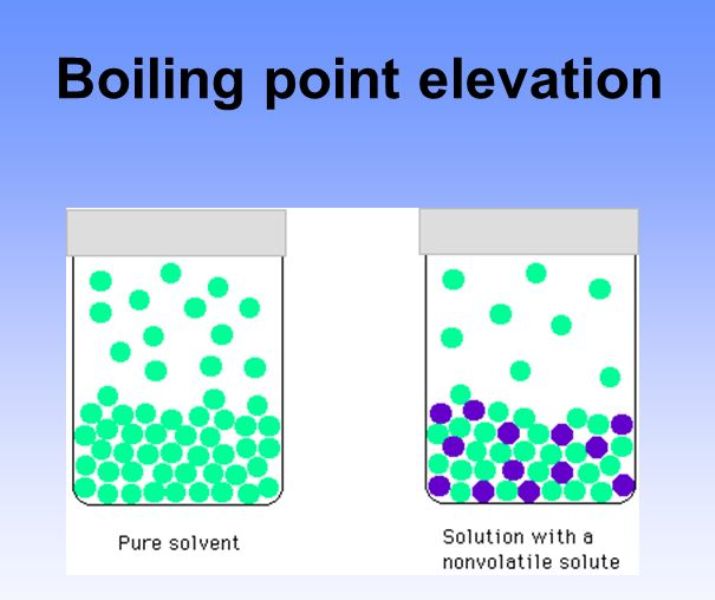
Boiling Point Drawing - For example, for water, the boiling point is 100ºc at a pressure of 1 atm. A boiling point diagram shows the boiling points of a binary mixture as a function of the vapour / liquid equilibrium of the mixture at constant pressure. So six carbons, and a higher boiling point, of 69 degrees c. Web the boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. Web boiling point and melting point. There are a variety of methods by which a sample's boiling point can be determined, including distillation, reflux, and by using a thiele tube. Therefore, we can compare the relative strengths of the imfs of the compounds to predict their relative boiling points. Web background if a sample of a liquid is placed in an otherwise empty space, some of it will vapourise, and the pressure in the space above the liquid will rise to some constant value. Boiling can be easily understood by the following experiment. (if you really care, the mystery fluids are water and isopropyl alcohol). Hexane has six carbons, one, two, three, four, five, and six. Web pentane has five carbons, one, two, three, four, five, so five carbons for pentane. Web mix of generic and real persons showing the five great powers of great britain, france, russia, germany and austria trying to. Can you determine the concentration of solute molecules in each of the three liquids? These can be found from the phase diagram by drawing a line across at 1 atmosphere pressure. Web draw the structures for the following amines in order of decreasing water solubility: A boiling point diagram shows the boiling points of a binary mixture as a function. Web pentane has five carbons, one, two, three, four, five, so five carbons for pentane. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. A) primary b) secondary c) secondary d) tertiary The boiling point at atmospheric pressure (14.7 psia, 1 bar absolute) for some common fluids and gases can be found from the table below:. Web the boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. Order these compounds from lowest to highest boiling point: The observable melting and boiling points of different organic molecules provides an additional illustration of the effects of noncovalent interactions. Web intermolecular forces (imfs) can be. Draw the enantiomer of this molecule. Can you determine the concentration of solute molecules in each of the three liquids? A boiling point diagram shows the boiling points of a binary mixture as a function of the vapour / liquid equilibrium of the mixture at constant pressure. Web normal melting and boiling points. Web water boiling at 99.3 °c (210.8. Draw the geometric isomer of this molecule. A) primary b) secondary c) secondary d) tertiary The stronger the imfs, the lower the vapor pressure of the substance and the higher the boiling point. (if you really care, the mystery fluids are water and isopropyl alcohol). Hexane has six carbons, one, two, three, four, five, and six. A) primary b) secondary c) secondary d) tertiary So six carbons, and a higher boiling point, of 69 degrees c. Under this condition, addition of heat results in the transformation of the liquid into its vapor without raising the temperature. The boiling point of a liquid varies depending upon the surrounding environmental pressure. The most straightforward method uses a thiele. Web what is boiling point diagram? As solute molecules are added to water, the boiling point increases. A boiling point diagram shows the boiling points of a binary mixture as a function of the vapour / liquid equilibrium of the mixture at constant pressure. When a substance boils, the molecules gain enough energy to “break free” of the other molecules. A) primary b) secondary c) secondary d) tertiary The observable melting and boiling points of different organic molecules provides an additional illustration of the effects of noncovalent interactions. The calculator below can be used to calculate the water boiling point at given absolute pressures. Hexane has six carbons, one, two, three, four, five, and six. Web pure water boils at. Melting and boiling are processes in. Web the boiling point of a substance is defined as the temperature at which a liquid becomes a gas. Dissolving a solute in a solvent increases the boiling point. So six carbons, and a higher boiling point, of 69 degrees c. Let’s takes water into an open container at room temperature. Draw a constitutional isomer of this. Boiling can be easily understood by the following experiment. Can you determine the concentration of solute molecules in each of the three liquids? Write down the boiling point temperature of your liquid as. The overarching principle involved is simple: Web determining boiling points from structure. As solute molecules are added to water, the boiling point increases. Dissolving a solute in a solvent increases the boiling point. Draw the geometric isomer of this molecule. Order these compounds from lowest to highest boiling point: Web pentane has five carbons, one, two, three, four, five, so five carbons for pentane. The observable melting and boiling points of different organic molecules provides an additional illustration of the effects of noncovalent interactions. (if you really care, the mystery fluids are water and isopropyl alcohol). Web the boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the saturated vapor pressure of a liquid is equal to the surrounding atmospheric pressure. If released to air, a vapor pressure of 96.9 mm hg at 25 °c indicates cyclohexane will exist solely in the vapor phase in the atmosphere. Web normal melting and boiling points.
Boiling point diagram YouTube
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/boiling-points-of-water-1328760-FINAL-c9c25739167d4722926f2caf69fbae7a.gif)
The Boiling Point of Water at Various Altitudes
Boiling Point Examples in Everyday Life StudiousGuy

What is Boiling Point Concept of Boiling Point Boiling Point
Thermal Secrets to Boiling Point Calibration

Boiling point in function of liquid composition of a mixture of ethanol
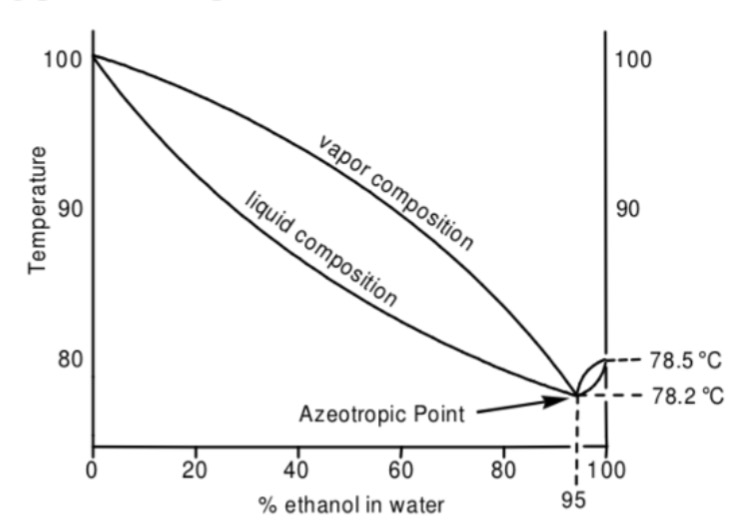
Boiling point of ethanol celsius

Boiling and Evaporation, Freezing and Melting Points of Water Stock

Boiling Point of Water What Temperature Does Water Boil?
Drawing Of Boiling Point , Free Transparent Clipart ClipartKey
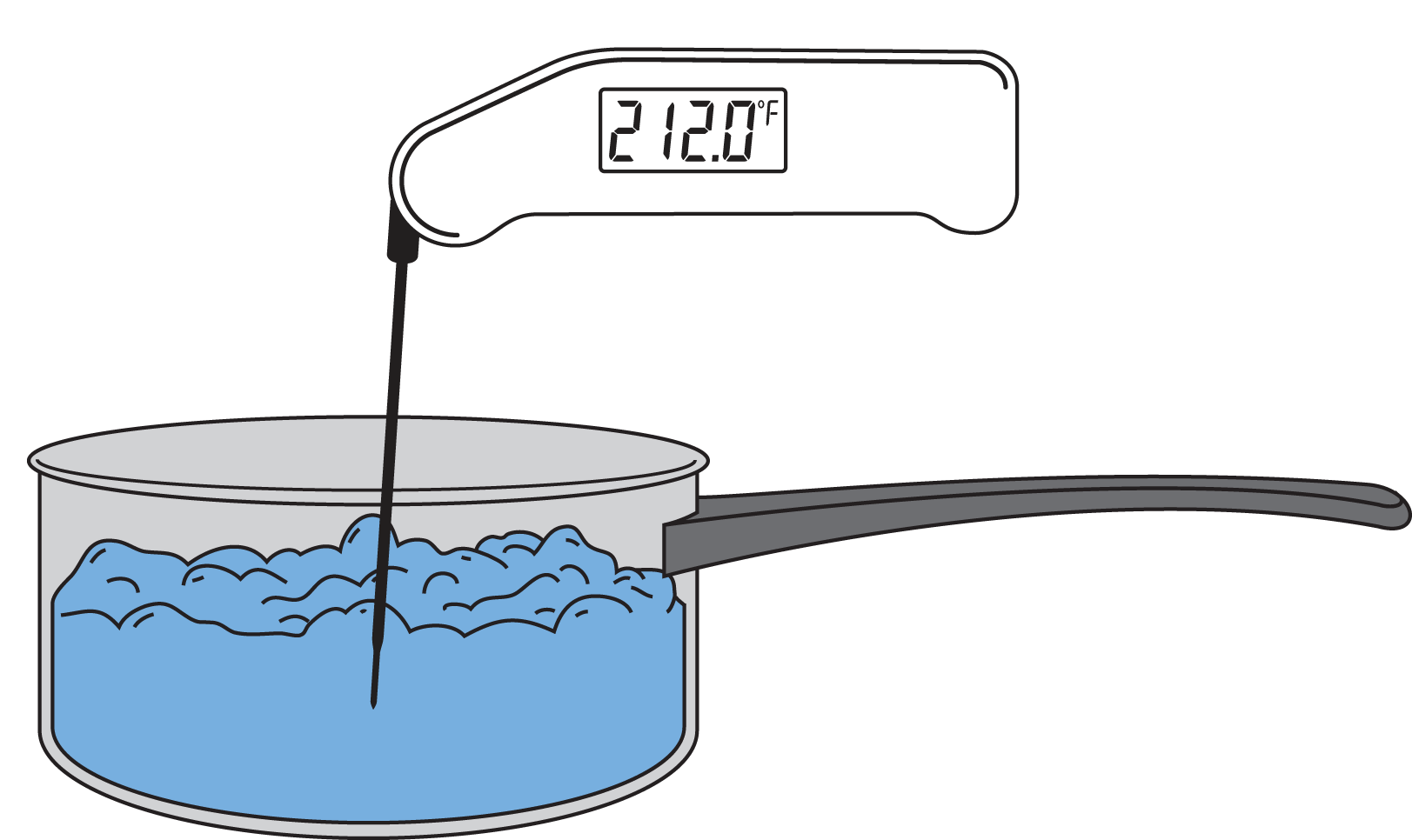
Web Water Boiling At 99.3 °C (210.8 °F) At 215 M (705 Ft) Elevation The Boiling Point Of A Substance Is The Temperature At Which The Vapor Pressure Of A Liquid Equals The Pressure Surrounding The Liquid [1] [2] And The Liquid Changes Into A Vapor.
For Example, For Water, The Boiling Point Is 100ºc At A Pressure Of 1 Atm.
Hexane Has Six Carbons, One, Two, Three, Four, Five, And Six.
Web Background If A Sample Of A Liquid Is Placed In An Otherwise Empty Space, Some Of It Will Vapourise, And The Pressure In The Space Above The Liquid Will Rise To Some Constant Value.
Related Post: