Draw And Label The Greenhouse Effect
Draw And Label The Greenhouse Effect - Then the gases, such as ozone, trap the heat that reflects back from the surface inside earth's atmosphere.the gases act like the. “greenhouse gases on the rise” Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the. Web drawing shows four different levels of ozone in the atmosphere. The sun’s radiations warm the plants and the air inside the greenhouse. Web in figure 3.1.1 the greenhouse effect is represented by the curved arrow showing 95% of the energy emitted by the earth’s surface that is reabsorbed, and the amount of ghgs in the atmosphere drive the size of this arrow. Web a greenhouse is a house made of glass that can be used to grow plants. Web test your knowledge of sea level rise and its effect on global populations. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes earth a. At top of stratosphere, 30 miles high, ozone absorbs most of the harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. Without the greenhouse effect, the surface of the earth would have an. The infrared radiative effect of all infrared absorbing constituents in the atmosphere. This model shows some of the other parts of the earth system that the greenhouse effect influences, including the water cycle and water. From initial stages of the process, the atmospheric structure and cloud coverage undergo significant changes, leading to an almost unstoppable and very. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes earth a. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (co 2 ), methane (ch 4 ), nitrous oxide (n 2 o), ozone (o 3 ), and fluorinated gases. At top. Greenhouse gases include carbon dioxide (co 2 ), methane (ch 4 ), nitrous oxide (n 2 o), ozone (o 3 ), and fluorinated gases. Web nitrous oxide water vapour is the largest contributor, responsible for 98 per cent of the natural greenhouse effect. This model shows some of the other parts of the earth system that the greenhouse effect influences,. Global warming is often described as the most recent example of climate change. Combustion of fuel produces many pollutants. This process makes earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere. In the middle of the tropsohere, ozone helps clean up certain pollutants. Web the greenhouse effect causes the atmosphere to retain heat gardeners that live in moderate or. The greenhouse effect happens when certain gases, which are known as greenhouse gases, accumulate in earth’s atmosphere. Web although the greenhouse effect is a natural phenomenon, there are concerns with something known as the enhanced greenhouse effect.the enhanced greenhouse effect is generally what is being talked about when people refer to the greenhouse effect and climate change.this effect refers to. In the middle of the tropsohere, ozone helps clean up certain pollutants. Web the past decade has been the hottest ever recorded since global temperature records began 150 years ago. At the top of the troposphere, 12 miles high, ozone acts as a greenhouse gas, trapping heat. Web greenhouse effect global warming describes the current rise in the average temperature. Web how does the greenhouse effect work? Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the. During the day the sun heats up the. Human activities are causing global warming. Web greenhouse gases include gases such as carbon dioxide (co 2), methane (ch 4), nitrous oxide (n 2 o), ozone (o 3), and fluorinated gases. Web in figure 3.1.1 the greenhouse effect is represented by the curved arrow showing 95% of the energy emitted by the earth’s surface that is reabsorbed, and the amount of ghgs in the atmosphere drive the size of this arrow. Web how does the greenhouse effect work? Web the past decade has been the hottest ever recorded since global temperature. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. Web use the tool to draw a greenhouse growing plants in cold weather. In the middle of the tropsohere, ozone helps clean up certain pollutants. Web how does the greenhouse effect work? The primary ghgs considered in this section are carbon dioxide (co 2), methane (ch 3),. This model shows some of the other parts of the earth system that the greenhouse effect influences, including the water cycle and water temperature. These greenhouse gases allow the sun's light to shine onto earth's surface. Web the greenhouse effect is the process through which heat is trapped near earth's surface by substances known as 'greenhouse gases.' imagine these gases. The greenhouse effect is one of the things that makes earth a. Web the greenhouse effect and our planet. Web greenhouse gases include gases such as carbon dioxide (co 2), methane (ch 4), nitrous oxide (n 2 o), ozone (o 3), and fluorinated gases. Web how does the greenhouse effect work? This model shows some of the other parts of the earth system that the greenhouse effect influences, including the water cycle and water temperature. Of those gases, known as greenhouse gases, water vapour has the largest effect. Web the greenhouse effect is a process that occurs when gases in earth's atmosphere trap the sun's heat. The sun’s radiations warm the plants and the air inside the greenhouse. Same is the case in the earth’s atmosphere. The infrared radiative effect of all infrared absorbing constituents in the atmosphere. Web test your knowledge of sea level rise and its effect on global populations. The heat trapped inside can’t escape out and warms the greenhouse which is essential for the growth of the plants. Solar energy absorbed at earth’s surface is radiated back into the atmosphere as heat. Web use the tool to draw a greenhouse growing plants in cold weather. This process makes earth much warmer than it would be without an atmosphere. Web the past decade has been the hottest ever recorded since global temperature records began 150 years ago.
Greenhouse Effect Diagram Quizlet
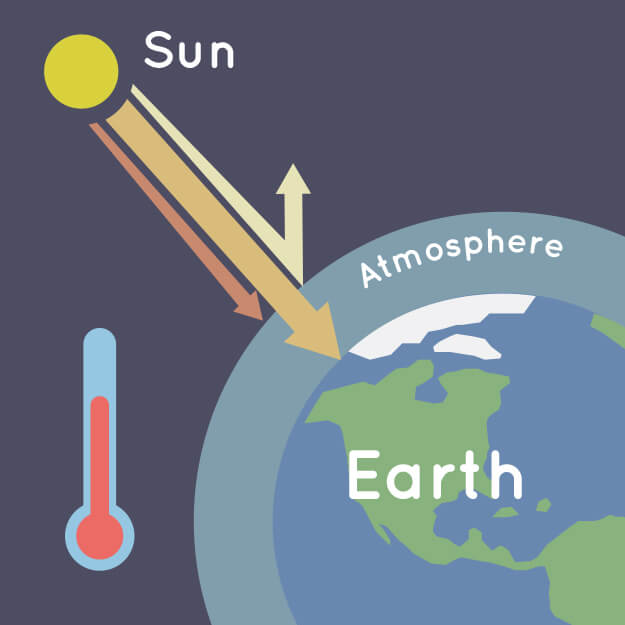
What Is the Greenhouse Effect? NASA Climate Kids
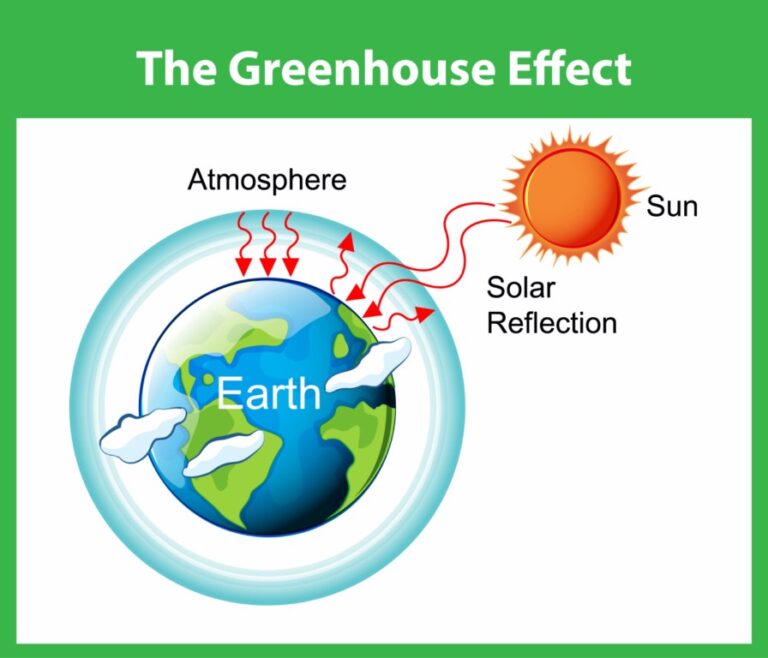
The Greenhouse effect diagram Seagrass Tech Private Limited

ESRL Global Monitoring Laboratory Education and Outreach

Greenhouse Effect
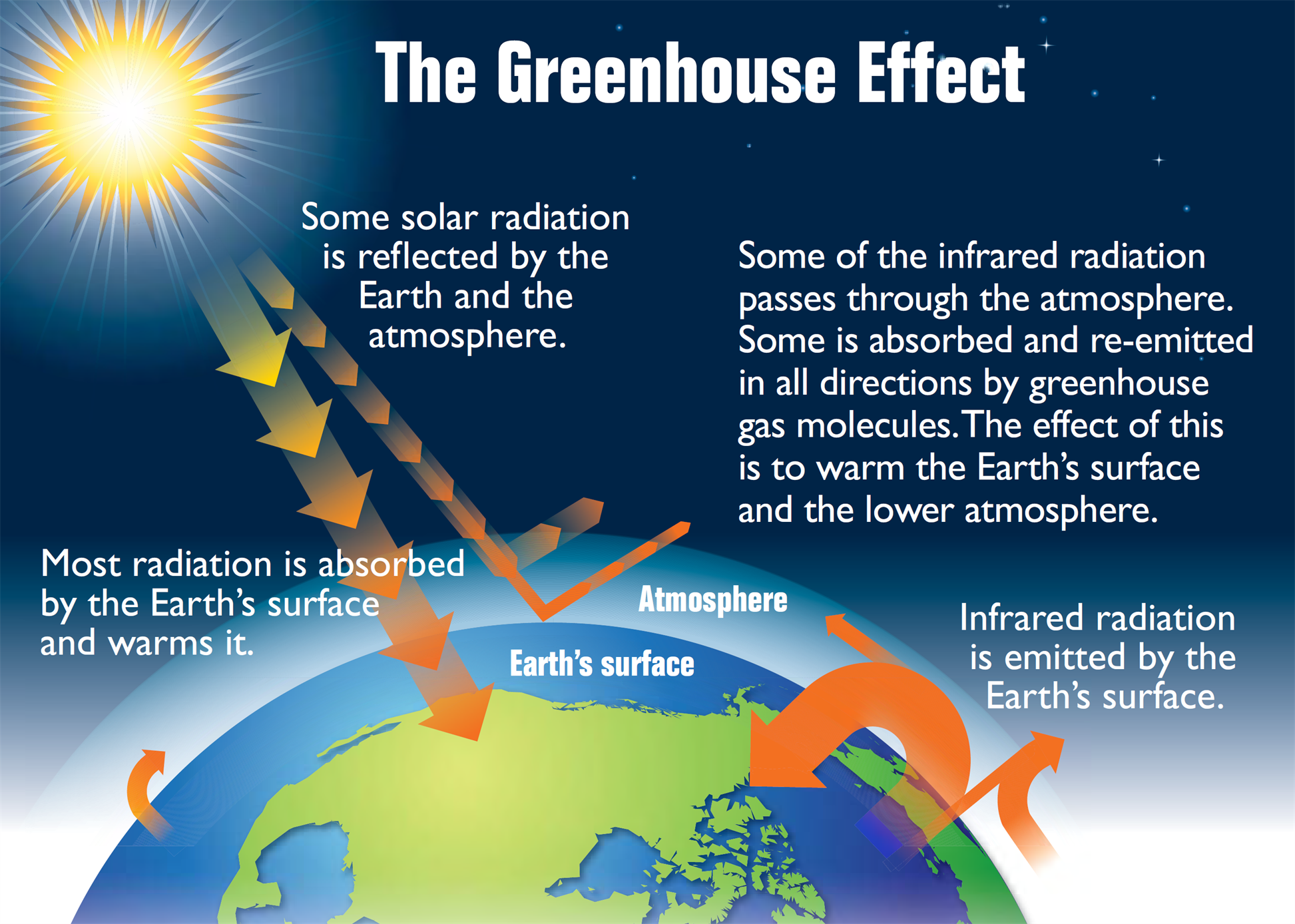
Global Warming and Greenhouse Effect Causes, Effects, and its Preventions

Earth's Greenhouse Effect NYS Dept. of Environmental Conservation

Greenhouse effect Definition, Diagram, Causes, & Facts Britannica
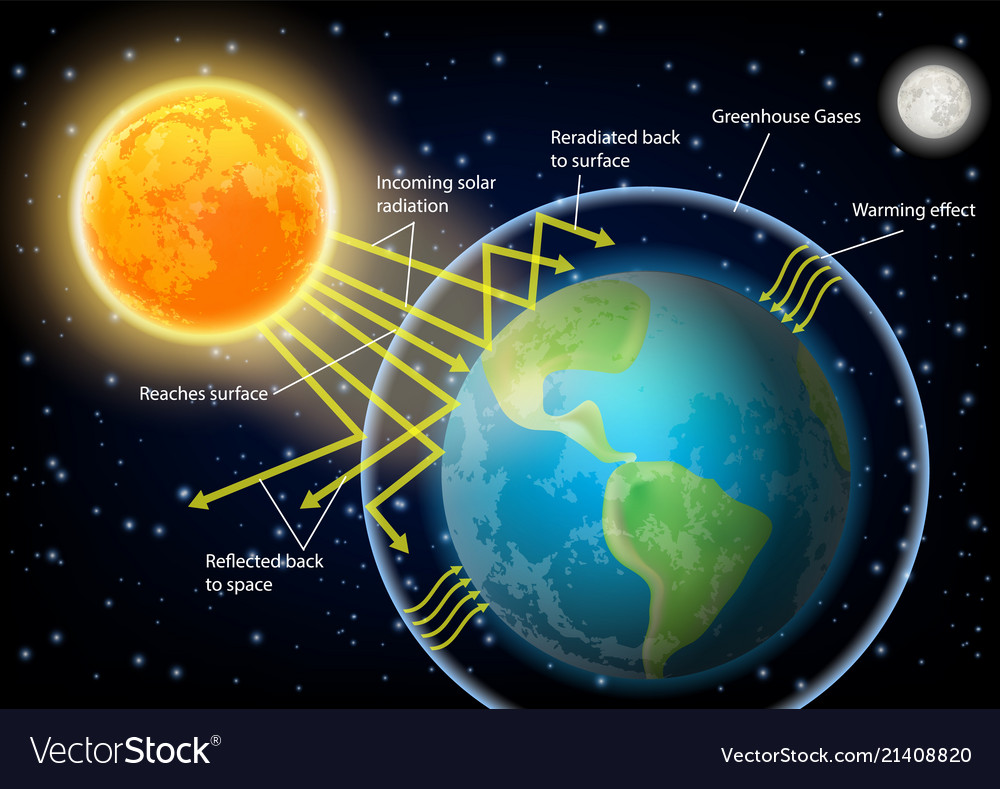
Greenhouse effect diagram Royalty Free Vector Image
Greenhouse Effect Vector Illustration Diagram Stock Illustration
Web Greenhouse Effect, A Warming Of Earth’s Surface And Troposphere (The Lowest Layer Of The Atmosphere) Caused By The Presence Of Water Vapour, Carbon Dioxide, Methane, And Certain Other Gases In The Air.
Web The Greenhouse Effect Causes The Atmosphere To Retain Heat Gardeners That Live In Moderate Or Cool Environments Use Greenhouses Because They Trap Heat And Create An Environment That Is Warmer Than Outside Temperatures.
The Greenhouse Effect Happens When Certain Gases, Which Are Known As Greenhouse Gases, Accumulate In Earth’s Atmosphere.
Then The Gases, Such As Ozone, Trap The Heat That Reflects Back From The Surface Inside Earth's Atmosphere.the Gases Act Like The.
Related Post:
