Draw Dna Replication
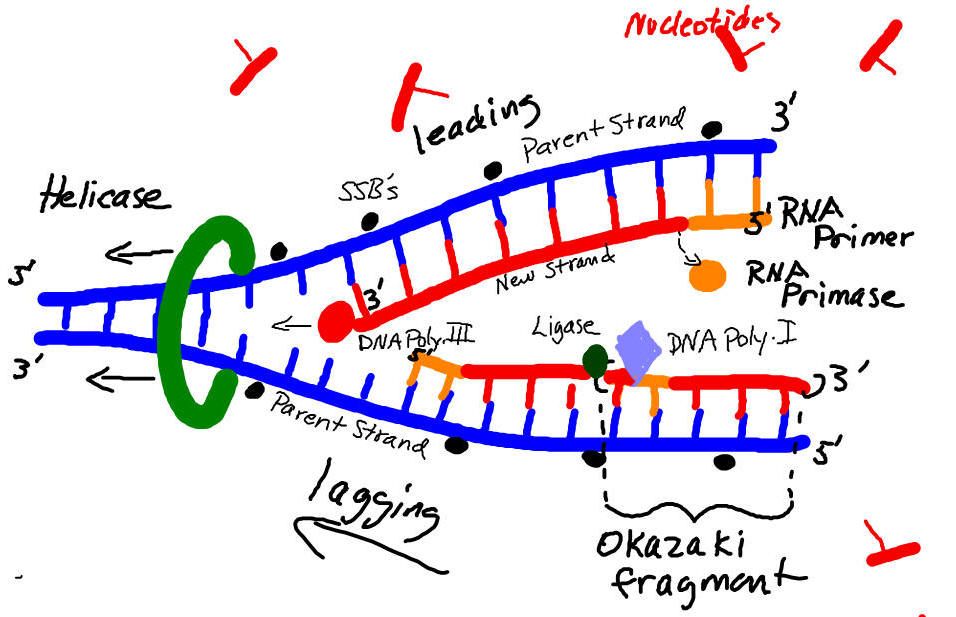
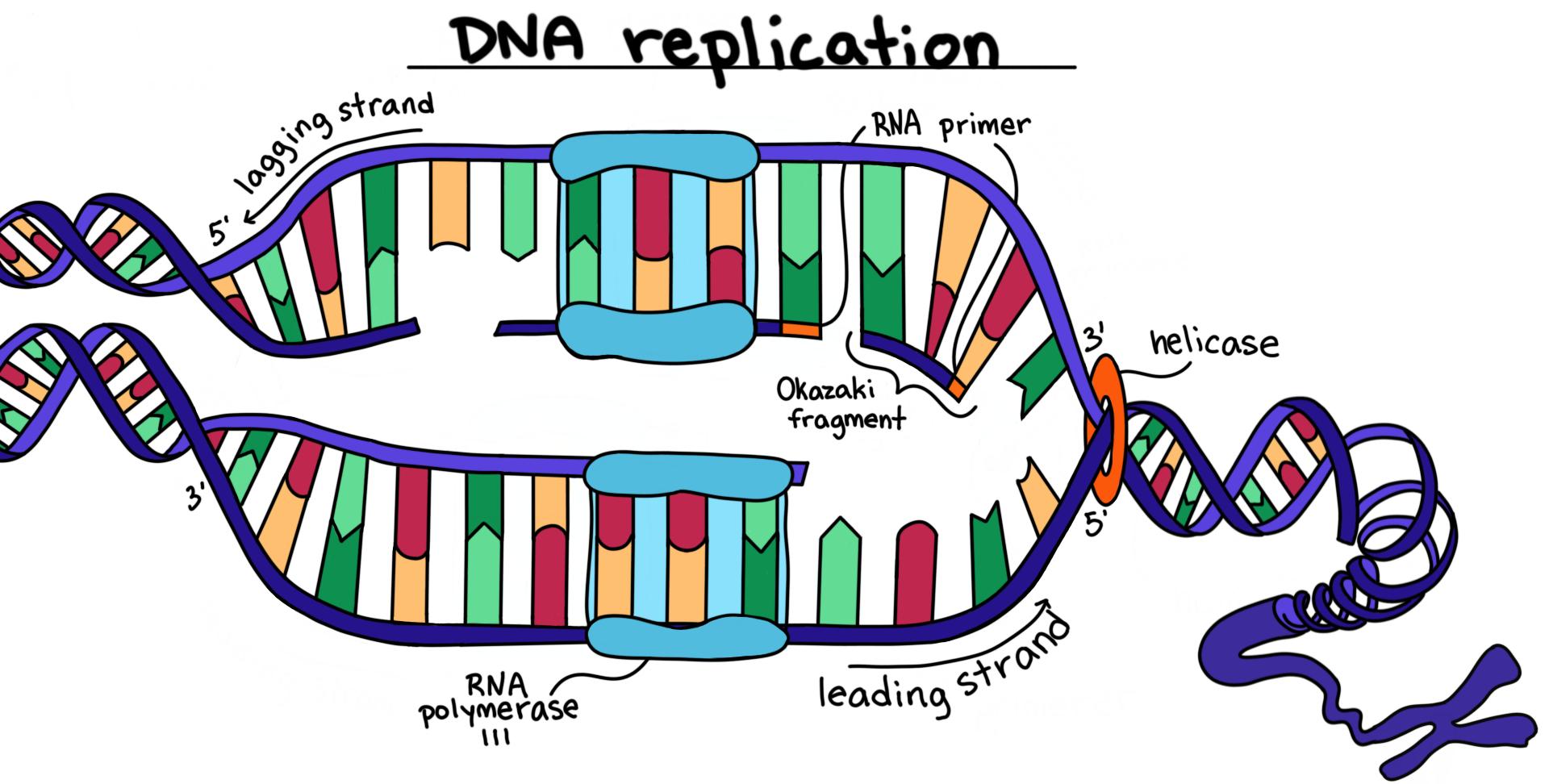
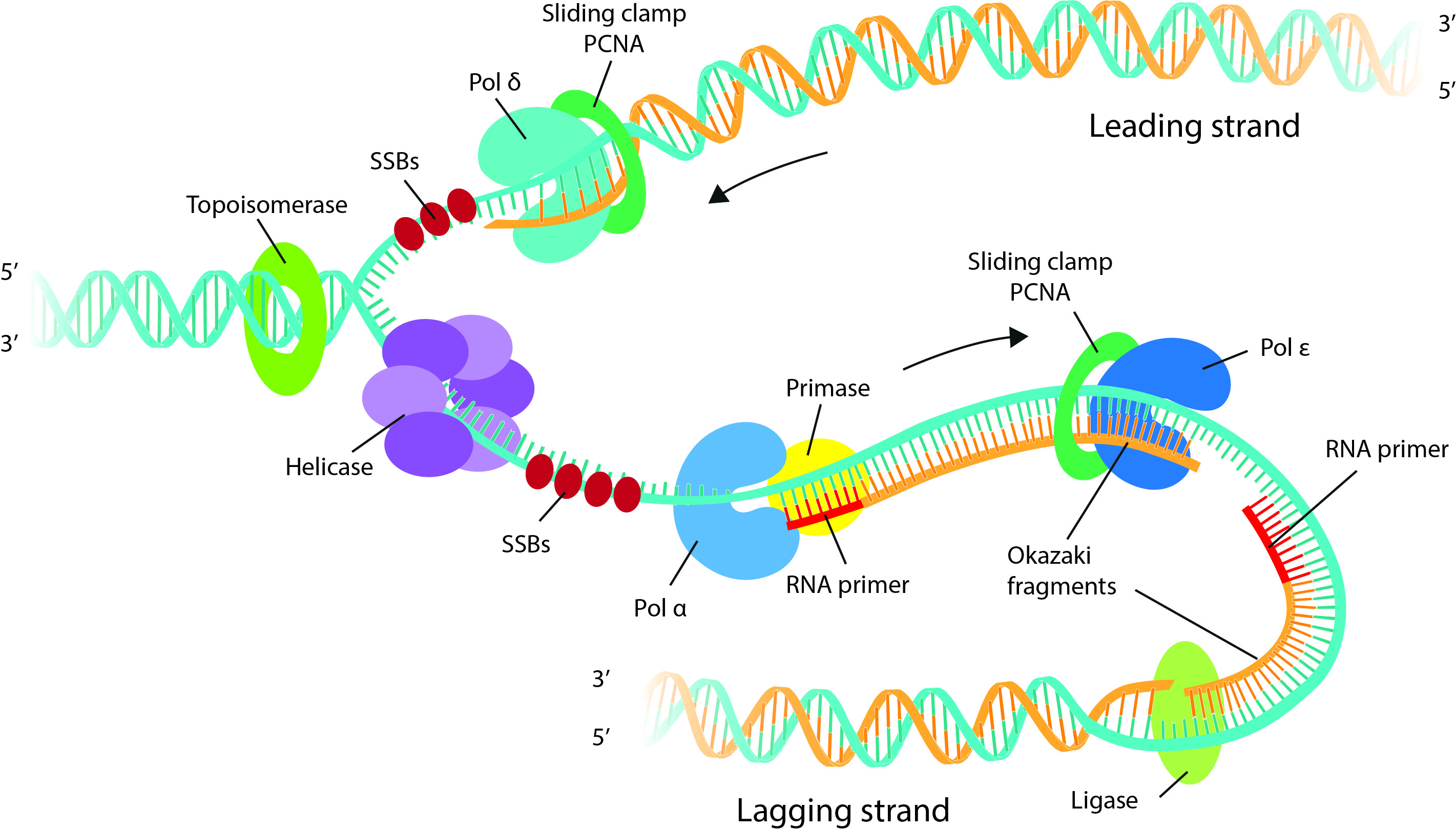
Draw Dna Replication - Web dna replication mechanisms all organisms must duplicate their dna with extraordinary accuracy before each cell division. Utilize and identify 5' and 3' directionality of dna and rna nucleotides and molecules. New dna is made by enzymes called dna polymerases, which require a template and a primer (starter) and synthesize dna in the 5' to 3' direction. Web dna replication uses a large number of proteins and enzymes ( ). Web dna replication polymerase chain reaction dna replication stage one the dna is unwound and unzipped. Primer binding the leading strand is the simplest to replicate. Draw and label a single dna polymerase iii on the leading strand 8. Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides. During cell division, each dna molecule has to be perfectly copied to ensure identical dna molecules to move to each of the two daughter cells. Primers are removed, new dna nucleotides are put in place of the primers. Build dna and rna nucleotides using puzzle pieces and compare their structures. Web dna replication steps initiation. Label the overall direction of dna replication 5. Before a cell divides, it must first copy (or replicate) its entire genome so that each resulting daughter cell ends up with its own complete genome. Web this is accomplished by the process of dna. Formation of replication fork step 2: Utilize and identify 5' and 3' directionality of dna and rna nucleotides and molecules. Web about transcript dna replication is a precise process where dna unwinds and splits into two strands. During cell division, each dna molecule has to be perfectly copied to ensure identical dna molecules to move to each of the two. Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides. Dna unwinds at the origin of replication. Each strand then serves as a template for a new dna molecule. Dozens enzymes and cofactors, acting precisely in an accurate amount carry on very specific roles for initiating replication process. Web dna replication updated: Web how dna replication works, easily explained with drawings. During cell division, each dna molecule has to be perfectly copied to ensure identical dna molecules to move to each of the two daughter cells. Replication fork formation before dna can be replicated, the double stranded molecule must be “unzipped” into. Web compare the structures of dna and rna. Draw and. The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how dna is copied. Web how dna replication works, easily explained with drawings. Draw and label helicase 4. Dozens enzymes and cofactors, acting precisely in an accurate amount carry on very specific roles for initiating replication process. Formation of replication fork step 2: Dna unwinds at the origin of replication. Dna replication is the process by which the genome’s dna is copied in cells. The replication of dna occurs during the synthesis phase, or s phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. Web compare the structures of dna and rna. Web this is accomplished by the process of. Dna replication demands a high degree of accuracy because even a minute mistake would result in mutations. Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides. Draw and label single stranded binding proteins 6. Web in molecular biology, [1] [2] [3] dna replication is the biological process of producing two identical replicas of dna from one original dna molecule. Web this. Web preparation for replication step 1: Web dna replication mechanisms all organisms must duplicate their dna with extraordinary accuracy before each cell division. Label the overall direction of dna replication 5. Web dna replication is the process in which dna is copied. Special molecules break the weak hydrogen bonds between. The elucidation of the structure of the double helix provided a hint as to how dna is copied. Dna replication begins when an enzyme, dna helicase, breaks the bonds between complementary bases in dna (see figure below ). Web about transcript dna replication is a precise process where dna unwinds and splits into two strands. Web replication of dna occurs. Termination okazaki fragments replication fork formation and its function leading strand the lagging strand applications of dna replication dna replication stress similarities between prokaryotic and eukaryotic dna replication The replication of dna occurs during the synthesis phase, or s phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. Each strand then serves as a template for a. Web dna replication steps initiation. Web dna replication uses a large number of proteins and enzymes ( ). Web compare the structures of dna and rna. Dozens enzymes and cofactors, acting precisely in an accurate amount carry on very specific roles for initiating replication process. There were three models for how organisms might replicate their dna: December 15, 2023 definition 00:00. Each strand in the double helix acts as a template for synthesis of a new, complementary strand. Web replication of dna occurs during the s phase of interphase and it further pushes the cell towards cell division (mitotic phase). The replication of dna occurs during the synthesis phase, or s phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. Web dna replication updated: It occurs during the synthesis (s) phase of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Utilize and identify 5' and 3' directionality of dna and rna nucleotides and molecules. Once the dna strands have been separated, a. The replication of dna occurs during the synthesis phase, or s phase, of the cell cycle, before the cell enters mitosis or meiosis. During cell division, each dna molecule has to be perfectly copied to ensure identical dna molecules to move to each of the two daughter cells. Recall that adenine nucleotides pair with thymine nucleotides.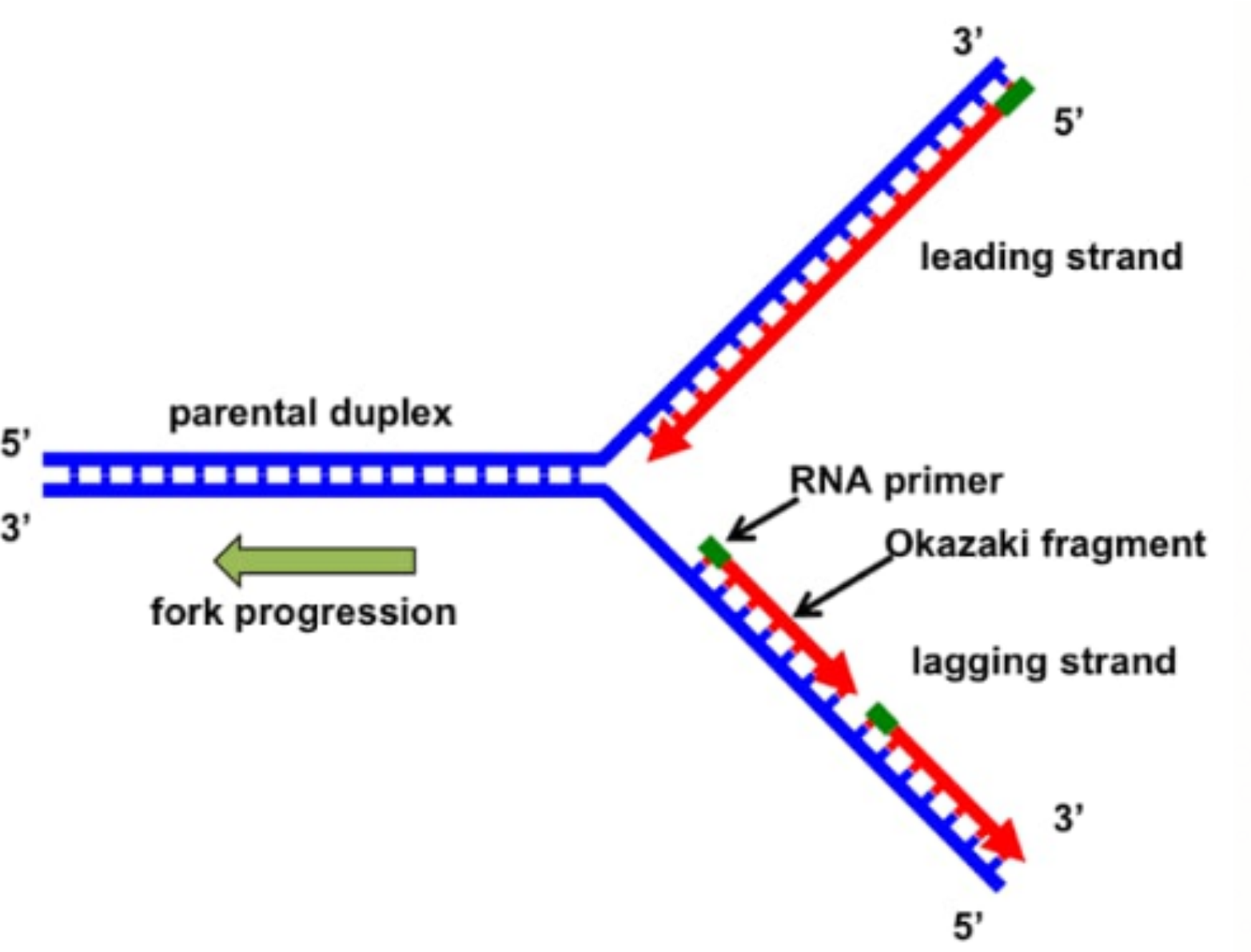
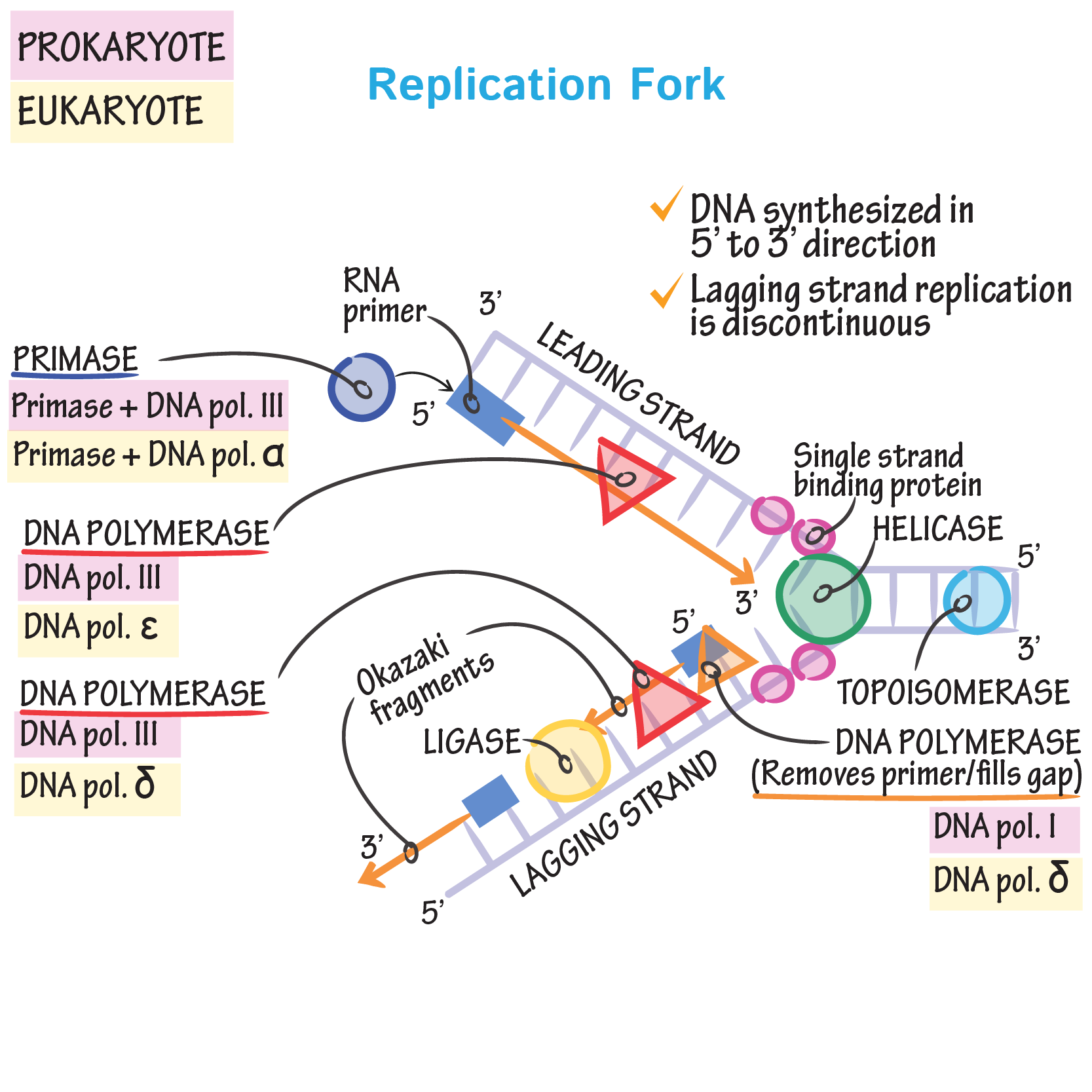
Draw a labelled schematic sketch of replication fork of DNA. Explain

SBK1013 INTRODUCTION TO BIOCHEMISTRY DNA REPLICATION
Dna Replication Drawing at Explore collection of
Process of DNA Replication Expii
DNA Replication Lagging Strand

DNA Structure & DNA Replication Biology Online Tutorial

DNA Replication Stages of Replication TeachMePhyiology
Dna Replication Drawing at Explore collection of

replication Britannica

Dna Replication Drawing at GetDrawings Free download
The Helix Structure Is Unwound.
Helicase Brings About The Procedure Of Strand Separation, Which Leads To The Formation Of The Replication Fork.
Draw And Label The Leading Strand 7.
Dna Replication Demands A High Degree Of Accuracy Because Even A Minute Mistake Would Result In Mutations.
Related Post: