Draw The Derivative Of A Graph
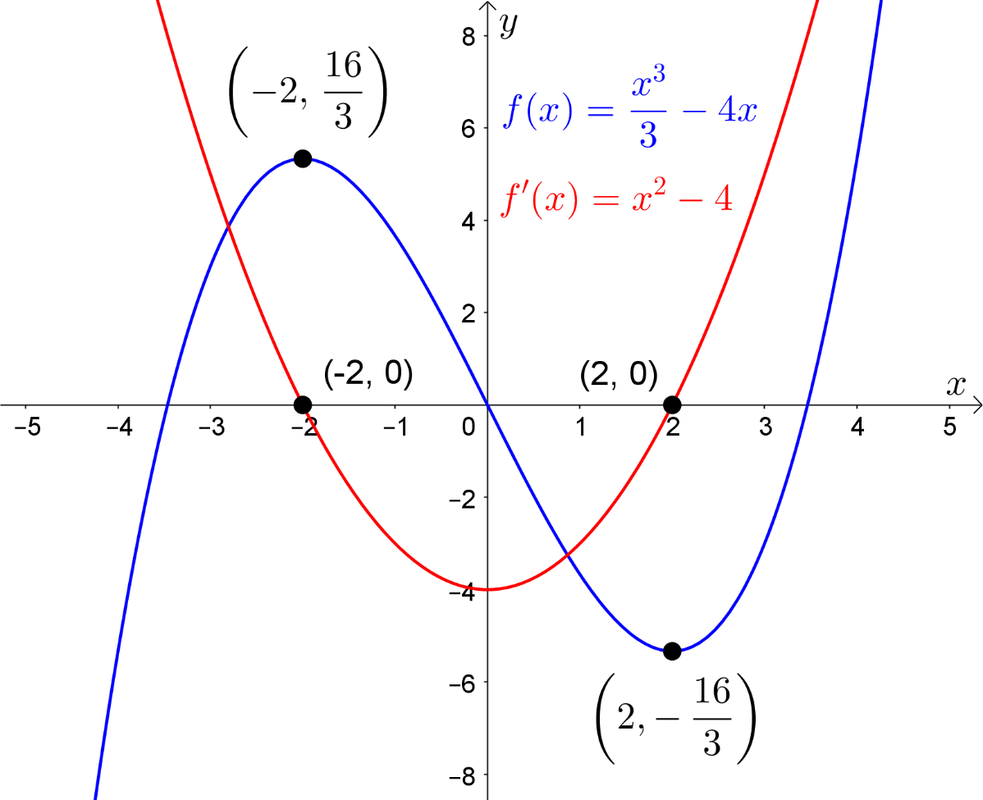
Draw The Derivative Of A Graph - Mark zeros at the locations of any turning points or stationary inflection points. Web for f(x) = − x3 + 3 2x2 + 18x, find all intervals where f is concave up and all intervals where f is concave down. Graph a derivative function from the graph of a given function. Web derivative graph rules below are three pairs of graphs. One of the main concepts in calculus. The derivative of a function f(x) is the function whose value at x is f ′ (x). Where f(x) has a tangent line with positive slope, f ′ (x) > 0. If the original graph is a circle, then the graph of the derivative will be similar (but opposite) to the purple math image you linked to. ( − ∞, 0) (0, 9 / 2) (9 / 2, ∞) we need to determine the sign of the derivative in each intervals. Graph functions, plot points, visualize algebraic equations, add sliders, animate graphs, and more. Given a function \(f\), use the following. Describe three conditions for when a function does not have a derivative. This relies on a solid understanding of functions, graphs, and the derivative as. Web sketching the derivative of a function. However, there is another issue to consider regarding the shape of the graph of a function. This video contains plenty of examples and. Typically, derivatives are introduced at the beginning of a calculus course and used throughout. Web for f(x) = − x3 + 3 2x2 + 18x, find all intervals where f is concave up and all intervals where f is concave down. Web these two critical points split the real line into 3 open. Connecting f, f', and f'' graphically. Web general drawing rules of derivative f’ (x) 1. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. Typically, derivatives are introduced at the beginning of a calculus course and used throughout. Web sketching the derivative of a function. This video contains plenty of examples and. Concavity and points of inflection. Describe three conditions for when a function does not have a derivative. Web we have shown how to use the first and second derivatives of a function to describe the shape of a graph. Given a function \(f\), use the following. Web the graphical relationship between a function & its derivative (part 2) connecting f and f' graphically. First, we learn how to sketch the derivative graph of a continuous, differentiable function f (x), either given the original function or its graph y=f (x). When you think you have a good representation of f ′ (x), click the show results! However,. Draw turning points at the location of any inflection points. Concavity and points of inflection. Place a straight object like your pencil on your original function’s curve where the points in “step 1” lie, to mimic. Drag the blue points up and down so that together they follow the shape of the graph of f ′ (x). Web we have. Concavity and points of inflection. Web the first derivative test provides an analytical tool for finding local extrema, but the second derivative can also be used to locate extreme values. The derivative of a function f(x) is the function whose value at x is f ′ (x). The top graph is the original function, f (x), and the bottom graph. Web the graphical relationship between a function & its derivative (part 2) connecting f and f' graphically. Web this calculus video tutorial explains how to sketch the derivatives of the parent function using the graph f (x). Graph a derivative function from the graph of a given function. Connecting f, f', and f'' graphically (another example) connecting f, f', and. Graph of derivative to original function what do you notice about each pair? We also know the behavior of \(f\) as \(x→±∞\). Using the second derivative can sometimes be a simpler method than using the first derivative. You can use d dx d d x or d dy d d y for derivatives. Describe three conditions for when a function. Web since acceleration is the derivative of velocity, you can plot the slopes of the velocity graph to find the acceleration graph. Where f(x) has a tangent line with positive slope, f ′ (x) > 0. Given a function \(f\), use the following. Another efficient way to implement derivative notation is by partnering it with. Web if the original graph. Web sketching the derivative of a function. Web we have shown how to use the first and second derivatives of a function to describe the shape of a graph. Given a function \(f\), use the following. Drawing the graph of a function. If the original graph is a circle, then the graph of the derivative will be similar (but opposite) to the purple math image you linked to. Web derivative graph rules below are three pairs of graphs. Much of calculus depends on derivatives and rates of change. Typically, derivatives are introduced at the beginning of a calculus course and used throughout. 👉 learn all about the applications of the derivative. Graph a derivative function from the graph of a given function. Connecting f, f', and f'' graphically (another example) connecting f, f', and f'' graphically. Web explore math with our beautiful, free online graphing calculator. When x < 0, x2 > 0 but (2x − 9) < 0, so f ′ (x) < 0 and the function is decreasing. This video contains plenty of examples and. One of the main concepts in calculus. Suppose we’re given the graph of a function and we want to find the graph of the original function.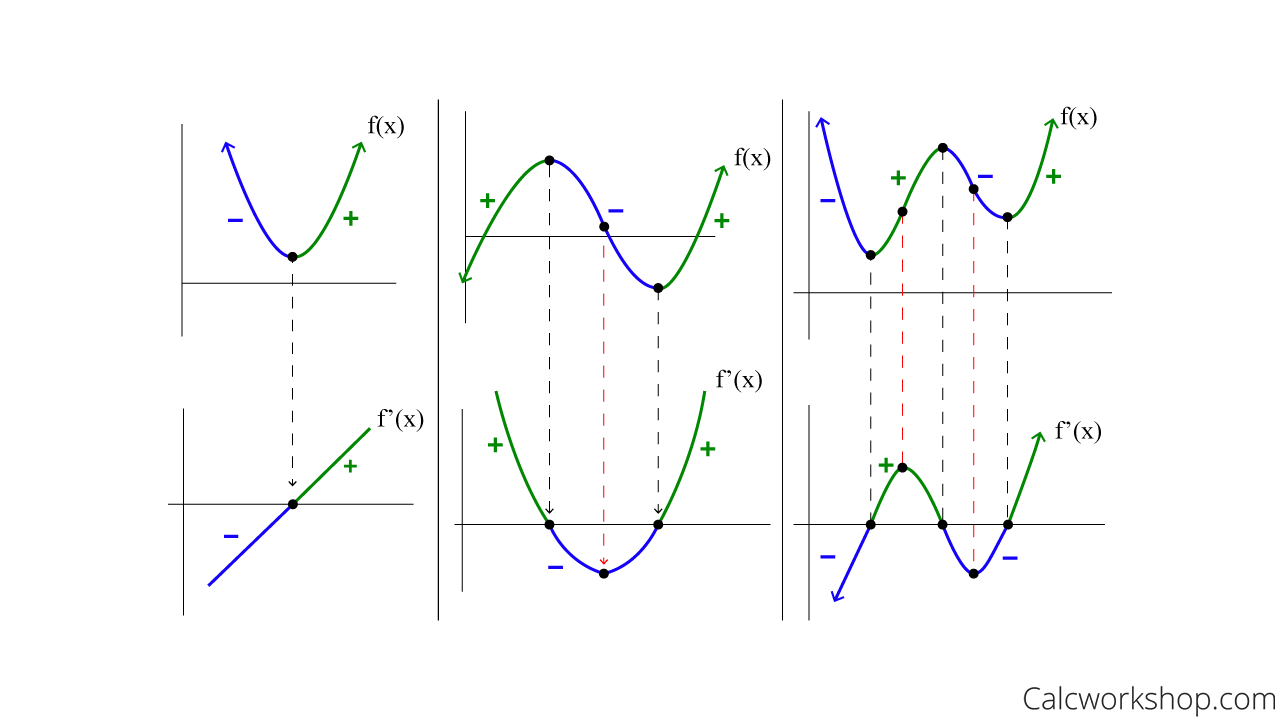
Derivative Graph Vs Original Function (w/ 15+ Examples!)
6D Graphs of derivative functions OLVER EDUCATION

Steps to Sketch Graph of Function From Derivative YouTube
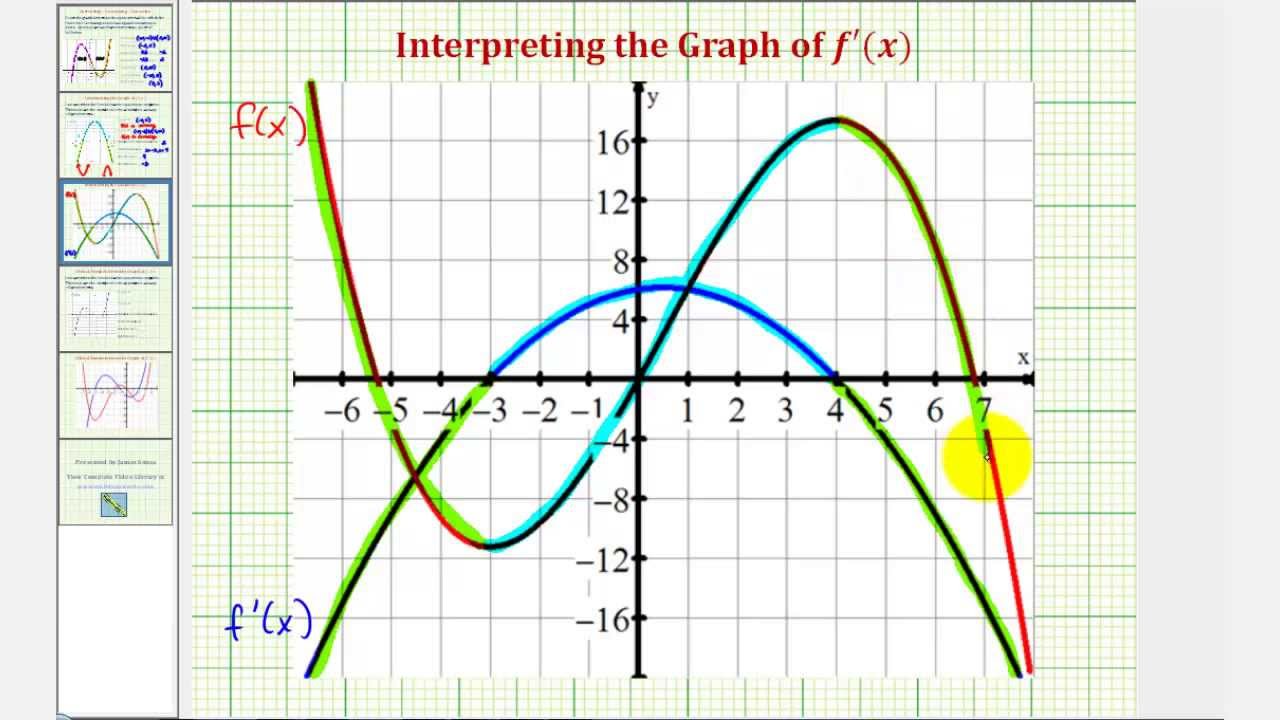
Ex 1 Interpret the Graph of the First Derivative Function Degree 2

Sketching the graph of a derivative, (as in d𝑦/d𝑥), A Level Maths, 12th

Drawing the Graph of a Derivative YouTube
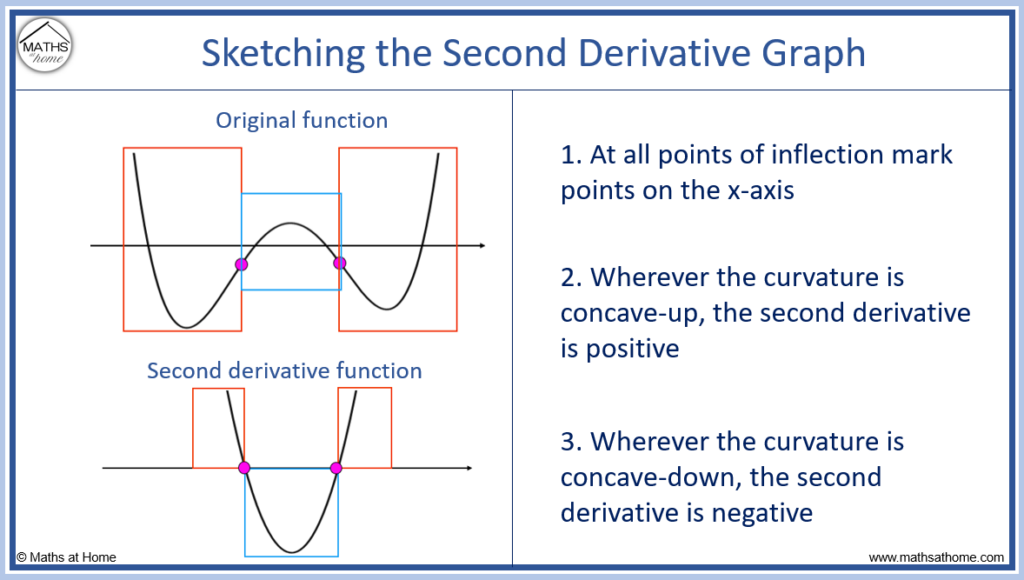
How to Sketch the Graph of the Derivative

How to sketch first derivative and Function from graph of second

Draw the Function given Graph of Derivative YouTube

Pin on Graphing The Derivative of a Function
Connecting F, F', And F'' Graphically.
However, There Is Another Issue To Consider Regarding The Shape Of The Graph Of A Function.
We Will Use That Understanding A.
The Derivative Of A Function F(X) Is The Function Whose Value At X Is F ′ (X).
Related Post: