How To Draw A Phospholipid
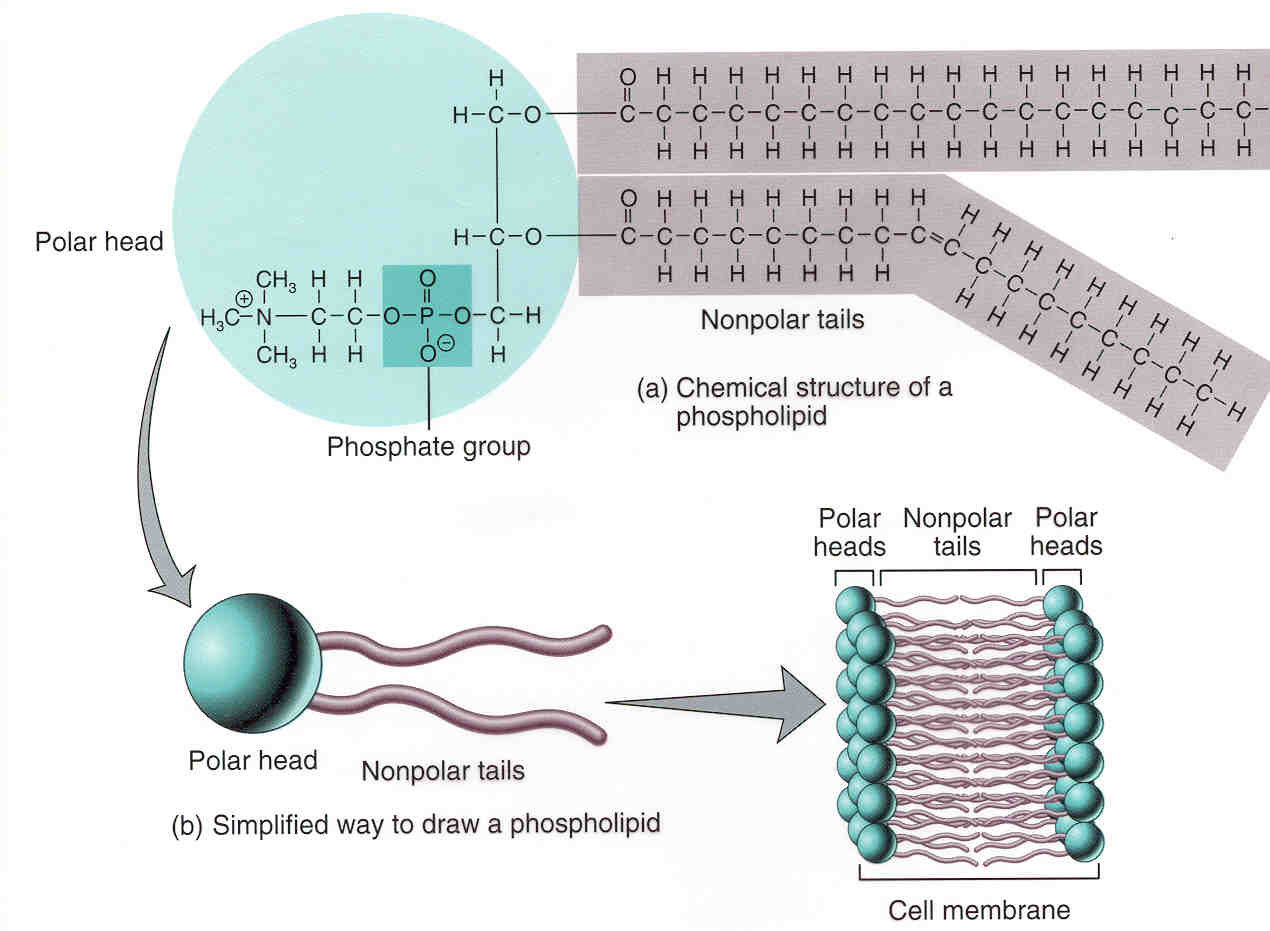
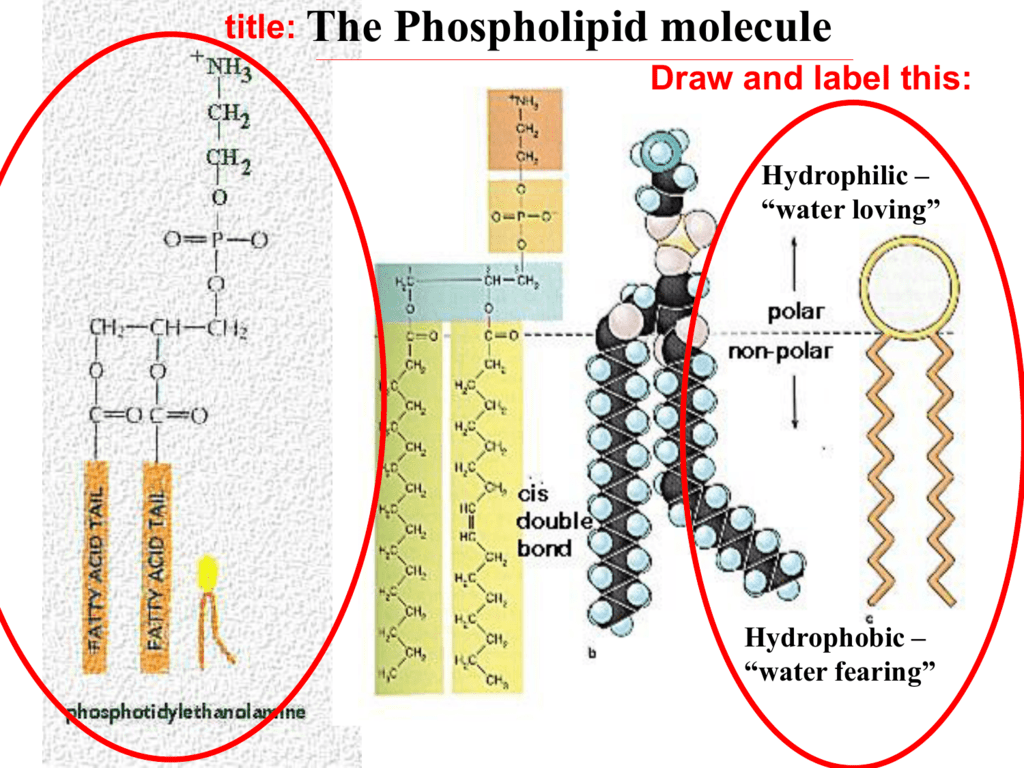
How To Draw A Phospholipid - Web what’s it made up of? Web a phospholipid is a molecule with two fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Each phospholipid is made up of two fatty acids, a phosphate group, and a glycerol molecule. The head and the two tails. Unsaturated fatty acids result in kinks in the hydrophobic tails. The phosphorylated component contains ethanolamine here. The phosphate may be modified by the addition of charged or polar chemical groups. Web a phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. Web 846 share 227k views 9 years ago cell membrane overview learn about the detailed structure of phospholipids in the cell membrane. The hydrophobic tails, each containing either a saturated or an unsaturated fatty acid, are long hydrocarbon chains. Web phosphatidic acid is converted into a glycerophospholipid by esterifying various groups, such as ethanolamine, serine, choline, inositol, and others to the phosphate of phosphatidic acid. Several chemical r groups may modify the phosphate. In water, phospholipids spontaneously form a double layer called a lipid bilayer, in which the hydrophobic tails of phospholipid molecules are sandwiched between two layers of.. Web what’s it made up of? In water, phospholipids spontaneously form a double layer called a lipid bilayer, in which the hydrophobic tails of phospholipid molecules are sandwiched between two layers of. Web a phospholipid is a lipid that contains a phosphate group. Several chemical r groups may modify the phosphate. Web google classroom overview of lipids, covering fats and. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. These compounds have a chiral center at c2 and have an r. The phospholipids form a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing outward. Web a phospholipid is a molecule with two fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Unsaturated fatty acids result in kinks in. Web phosphatidic acid is converted into a glycerophospholipid by esterifying various groups, such as ethanolamine, serine, choline, inositol, and others to the phosphate of phosphatidic acid. The head and the two tails. And all of this is held together by glycerol backbone. This phospholipid contains hexahydric alcohol called inositol in its phosphorylated component. This sketch of a phospholipid molecule shows. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. Web the phospholipids are not true fats because they have one of the fatty acids replaced by a phosphate group. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. The head. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. The cell membrane is primarily made up of three things: Web a phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. It has that polar phosphate head group, and it has two fatty acid. Introduction we sometimes talk about fat as if it were a malevolent substance bent on our dietary destruction. This sketch of a phospholipid molecule shows two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Web what’s it made up of? The phosphorylated component contains ethanolamine here. A phospholipid is a lipid that contains a phosphate group and. The key molecule in the membrane is a phospholipid. Web what’s it made up of? The cell membrane is primarily made up of three things: Several chemical r groups may modify the phosphate. This sketch of a phospholipid molecule shows two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Several chemical r groups may modify the phosphate. Web the phospholipids are not true fats because they have one of the fatty acids replaced by a phosphate group. The phospholipids form a bilayer with the hydrophilic heads facing outward. Stearic acid is shown as the fatty acid, but there are many variations in the fatty acids. Web phosphatidic acid is. Biological membranes usually involve two layers of phospholipids with their tails pointing inward, an arrangement called a phospholipid bilayer. Web in this video, we're going to actually explore in detail the structure of phospholipids in our cell membrane. Web google classroom overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Web a phospholipid. The phosphorylated component contains ethanolamine here. Proteins 1) phospholipids there are two important parts of a phospholipid: The cell membrane is primarily made up of three things: The phosphate may be modified by the addition of charged or polar chemical groups. Web this tutorial demonstrates how to draw lipid bilayer in powerpoint for research publication, conference posters, science figures and graphical abstracts. Web a phospholipid is an amphipathic molecule which means it has both a hydrophobic and a hydrophilic component. The hydrophobic tails, each containing either a saturated or an unsaturated fatty acid, are long hydrocarbon chains. Web about press copyright contact us creators advertise developers terms privacy policy & safety how youtube works test new features nfl sunday ticket press copyright. This sketch of a phospholipid molecule shows two fatty acids and a phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Unsaturated fatty acids result in kinks in the hydrophobic tails. Web google classroom overview of lipids, covering fats and oils, saturated and unsaturated fats, triglycerides (triacylglycerols), phospholipids, and steroids. Web this short clip from the lesson lipids: The hydrophilic (polar) head group and hydrophobic tails (fatty acid chains) are depicted in the single phospholipid molecule. A phospholipid is a type of lipid molecule that is the main component of the cell membrane. Web a phospholipid is a molecule with two fatty acids and a modified phosphate group attached to a glycerol backbone. Web phosphatidic acid is converted into a glycerophospholipid by esterifying various groups, such as ethanolamine, serine, choline, inositol, and others to the phosphate of phosphatidic acid.
Phospholipids Introduction to Chemistry

Components and Structure OpenStax Biology 2e
Phospholipid Bilayer Introduction, Structure and Functions

Phospholipid Structure Labeling Diagram Quizlet
On the back of it draw and label the phospholipid
Illustrated Glossary of Organic Chemistry Phospholipid bilayer
/phospholipid_molecule-58adc6f95f9b58a3c9d1143f.jpg)
How Phospholipids Help Hold a Cell Together

How to Draw a Phospholipid Bilayer YouTube

Lipids Microbiology

Phospholipid bilayers made easy Science is Delicious
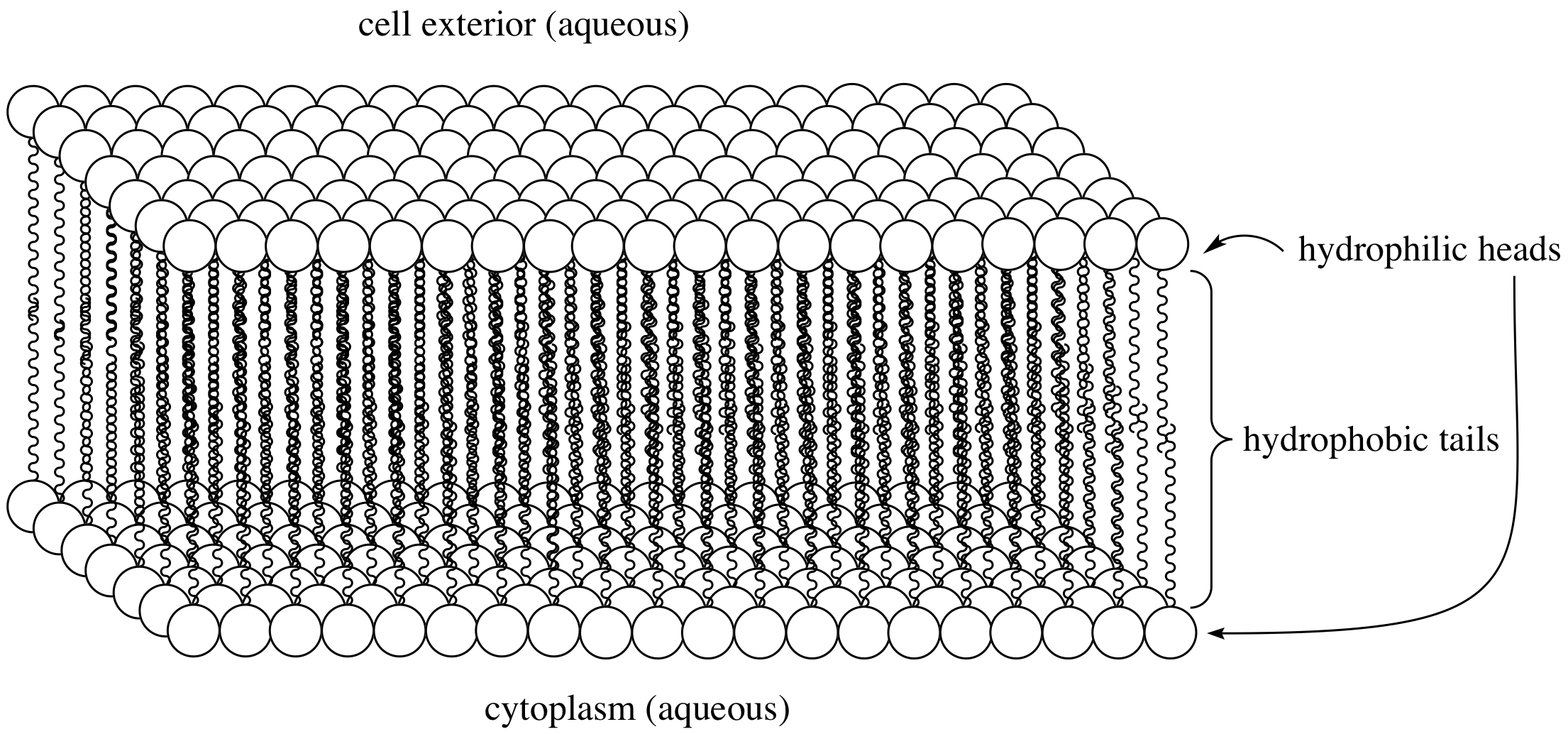
Biological Membranes Usually Involve Two Layers Of Phospholipids With Their Tails Pointing Inward, An Arrangement Called A Phospholipid Bilayer.
Each Phospholipid Is Made Up Of Two Fatty Acids, A Phosphate Group, And A Glycerol Molecule.
Web The Phospholipids Are Not True Fats Because They Have One Of The Fatty Acids Replaced By A Phosphate Group.
Web This Phospholipid Molecule Is Composed Of A Hydrophilic Head And Two Hydrophobic Tails.
Related Post: