How To Draw A Ray Diagram
How To Draw A Ray Diagram - Web a ray diagram is a tool that is used to determine the location, size, orientation, and type of image formed by a mirror. Beyond the lens, it will pass through the principal focal point. Second, we draw light rays from the image to the eye the image is virtual. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. Once through the lens, the ray should. Let's begin with the task of drawing a ray diagram to show how suzie will be able to see the image of the green object arrow in the diagram below. Web shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. These diagrams can be used to find the position and size of the image and whether that image is real or virtual. Also, an arrow on the tip of the ray shows the direction of propagation of light. Web first, we draw an image of the object on the other side of the mirror distance a is equal to distance b and the image size is the same size as the object size. Web a ray from the top of the object proceeding parallel to the centerline perpendicular to the lens. Web in a ray diagram, you draw. We'll go through the do's and don'ts and practice drawing diagrams f. A ray diagram must be drawn with a ruler, as all of the rays of light must be straight lines. Web this physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. In this lesson, we will see a similar method for constructing ray diagrams for. For example, you can draw a ray of light parallel to the principal axis which reflects off the mirror and passes through the principal focus (like in this video). Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can. Draw a ray which passes from the object through the centre of the lens. Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). Web in a ray diagram, you draw each ray as: There are a few important things to note: Also, an arrow on the tip of. Web this physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Web draw kinematic arrangement diagram and ray diagram for 6 speed gear box, with the minimum speed of 56rpm and maximum speed of 800rpm. Table of contents what is a mirror? Web drawing a ray diagram. Web shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Web this physics video tutorial on optics. Light travels in straight lines within a uniform medium (this means that light can change direction upon entering a different medium). Web how do you draw a ray diagram? Broken lines from the image to mirror indicate virtual rays. Once through the lens, the ray should. Web a ray diagram is a tool that is used to determine the location,. A ray through the center of the lens, which will be undeflected. Draw the object relative to. H reviews the three rules of refraction for converging lenses and demonstrates how to use the rules to draw a ray diagram for varying locations along t. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards. Web by examining the ray diagram of a spherical mirror, we can gain insights into the fascinating phenomena of reflection and image formation. A ray diagram must be drawn with a ruler, as all of the rays of light must be straight lines. Web how do you draw a ray diagram? With an arrowhead pointing in the direction that the. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw three incident rays traveling towards the lens. Once through the lens, the ray should pass through the principal focus. Web drawing a ray diagram. Pick a point on the top of the object and draw two incident rays traveling towards the mirror. We can use ray diagrams to understand. H reviews the three rules of refraction for converging lenses and demonstrates how to use the rules to draw a ray diagram for varying locations along t. This is because light only travels in straight lines. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Ray diagrams for concave mirrors were drawn in lesson 3. Web shows how to draw ray diagrams to locate the image formed by a convex lens. Web drawing a ray diagram. How to draw ray diagram i hope you enjoy this online lecture on how to draw ray. Web by examining the ray diagram of a spherical mirror, we can gain insights into the fascinating phenomena of reflection and image formation. Web draw kinematic arrangement diagram and ray diagram for 6 speed gear box, with the minimum speed of 56rpm and maximum speed of 800rpm. Draw a ray which passes from the object through the centre of the lens. Once through the lens, the ray should. These are the steps you follow to draw a ray diagram: We can use ray diagrams to understand how lenses work and to identify the location of the image formed. For a negative lens, it will proceed from the lens as if it emanated from the focal point on the near side of the lens. For example, you can draw a ray of light parallel to the principal axis which reflects off the mirror and passes through the principal focus (like in this video). Draw the object relative to.
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo
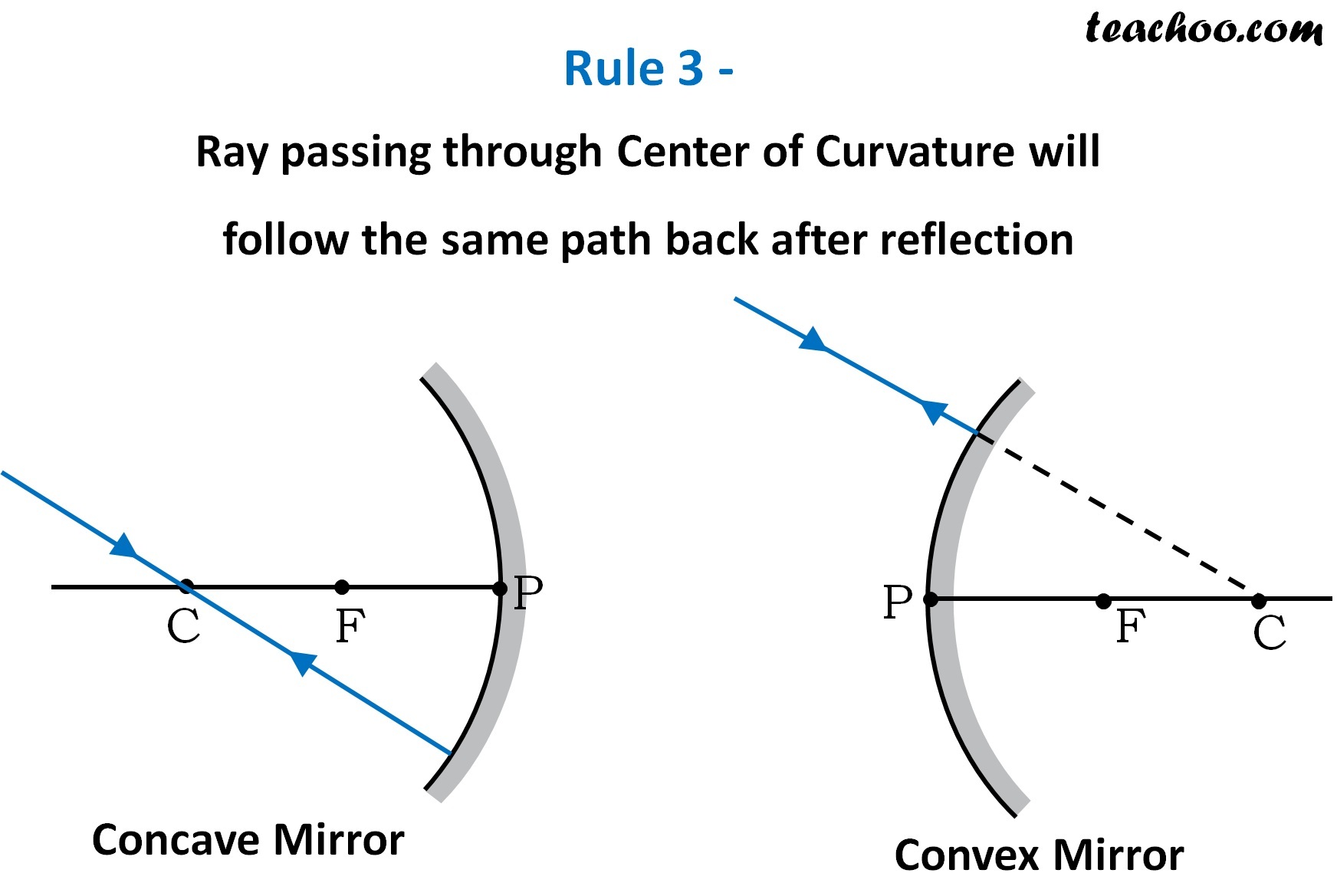
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

How to Draw Ray Diagrams for Convex Mirrors YouTube
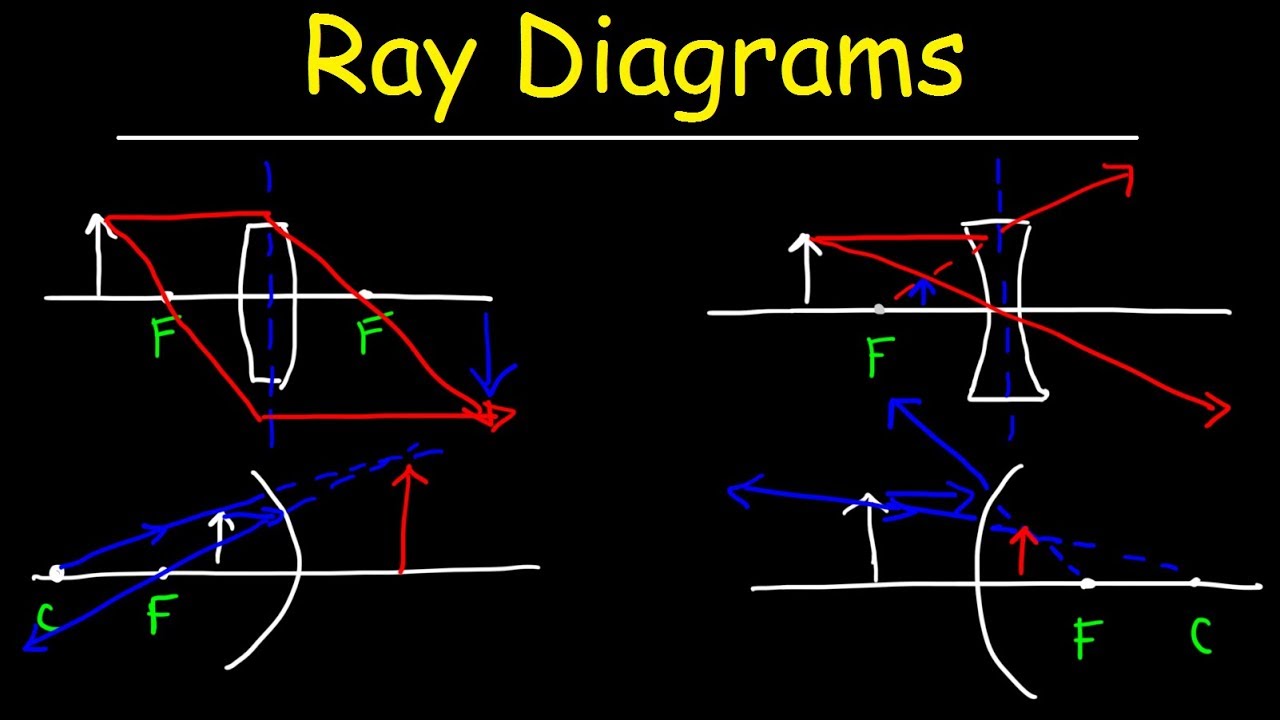
Ray Diagrams YouTube
Ray diagrams for convex mirrors

How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10
How to Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT)

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
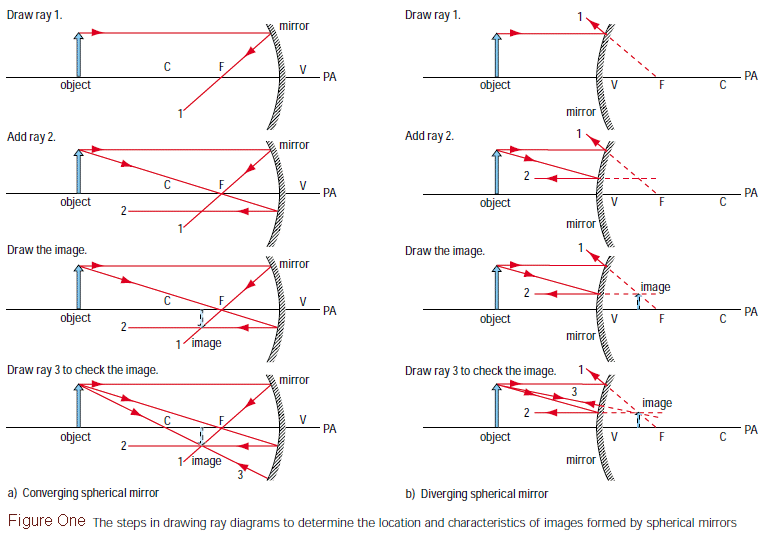
My Physics Webschool Ray Diagram
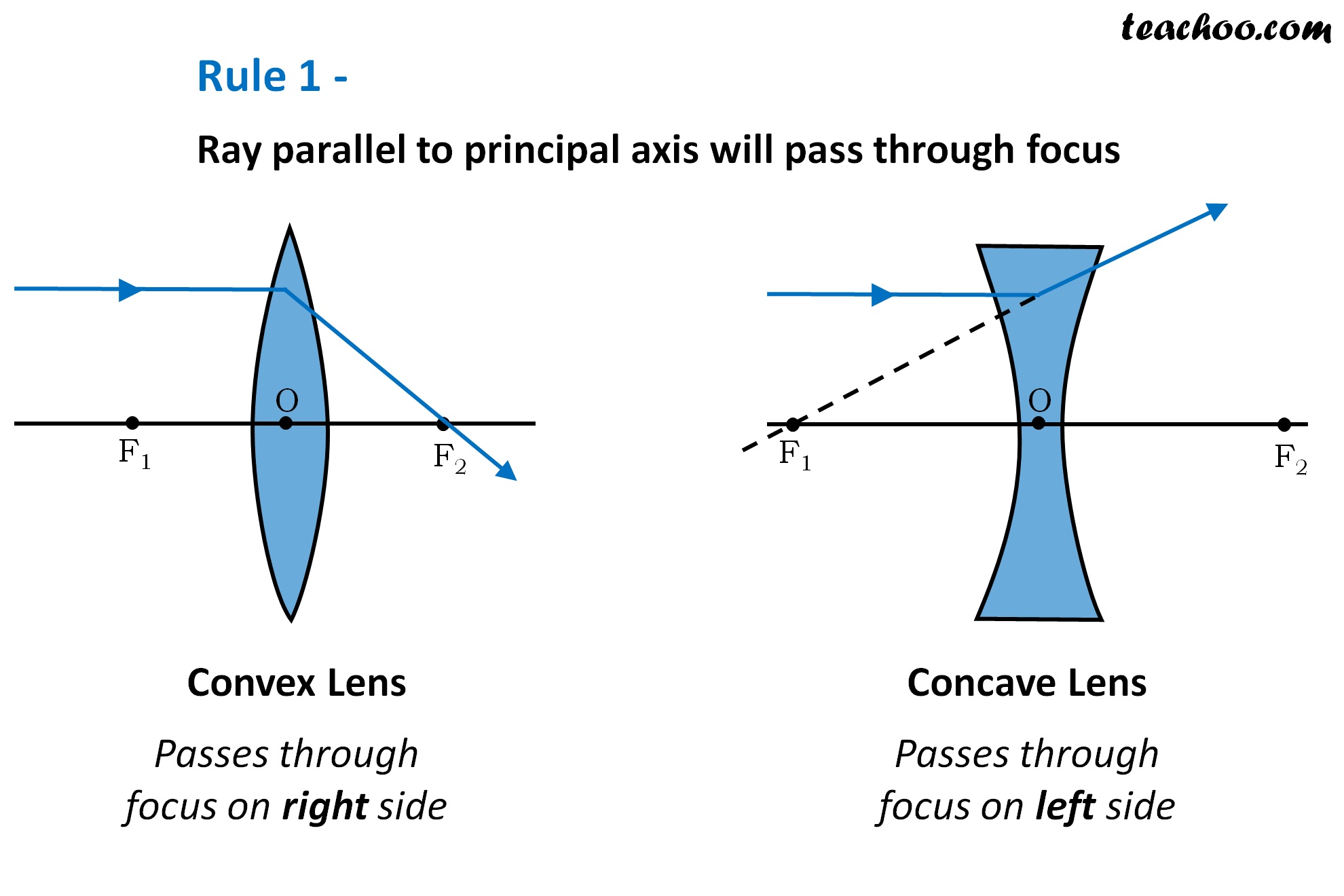
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
Draw The Plane Mirror As A Straight Line On A Principal Axis.
Beyond The Lens, It Will Pass Through The Principal Focal Point.
Once These Incident Rays Strike The Mirror, Reflect Them According To The Two Rules Of Reflection For Concave Mirrors.
Light Travels In Straight Lines Within A Uniform Medium (This Means That Light Can Change Direction Upon Entering A Different Medium).
Related Post:
.PNG)
