Microwave Radiation Drawing
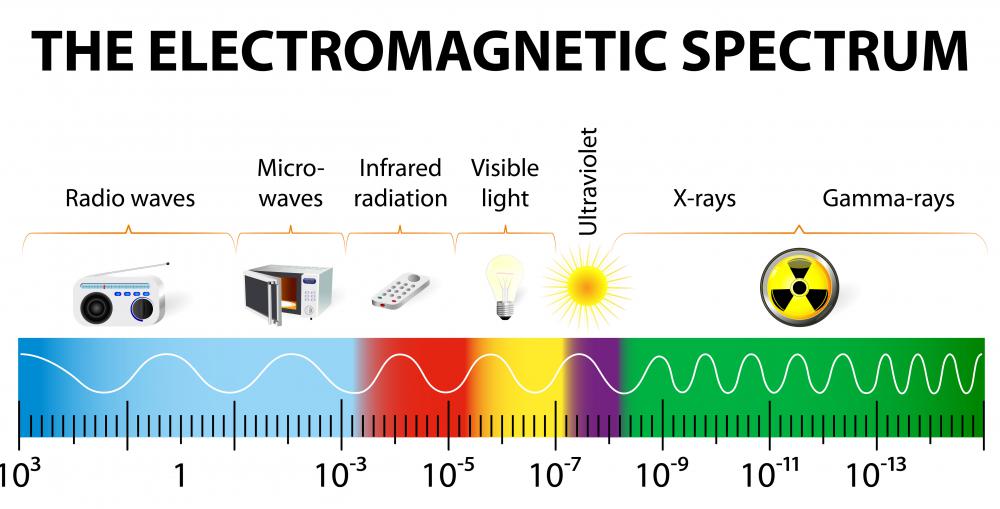
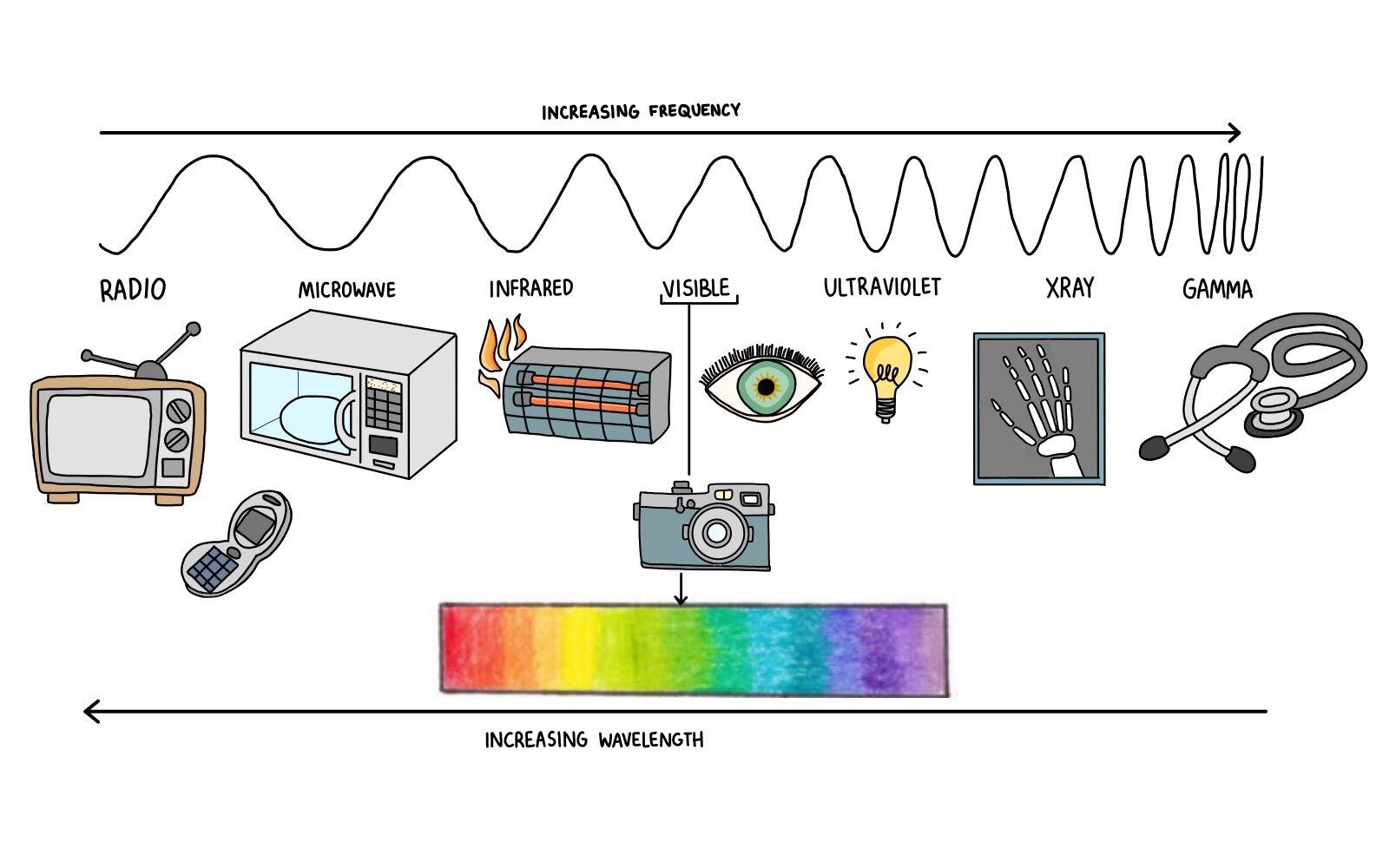
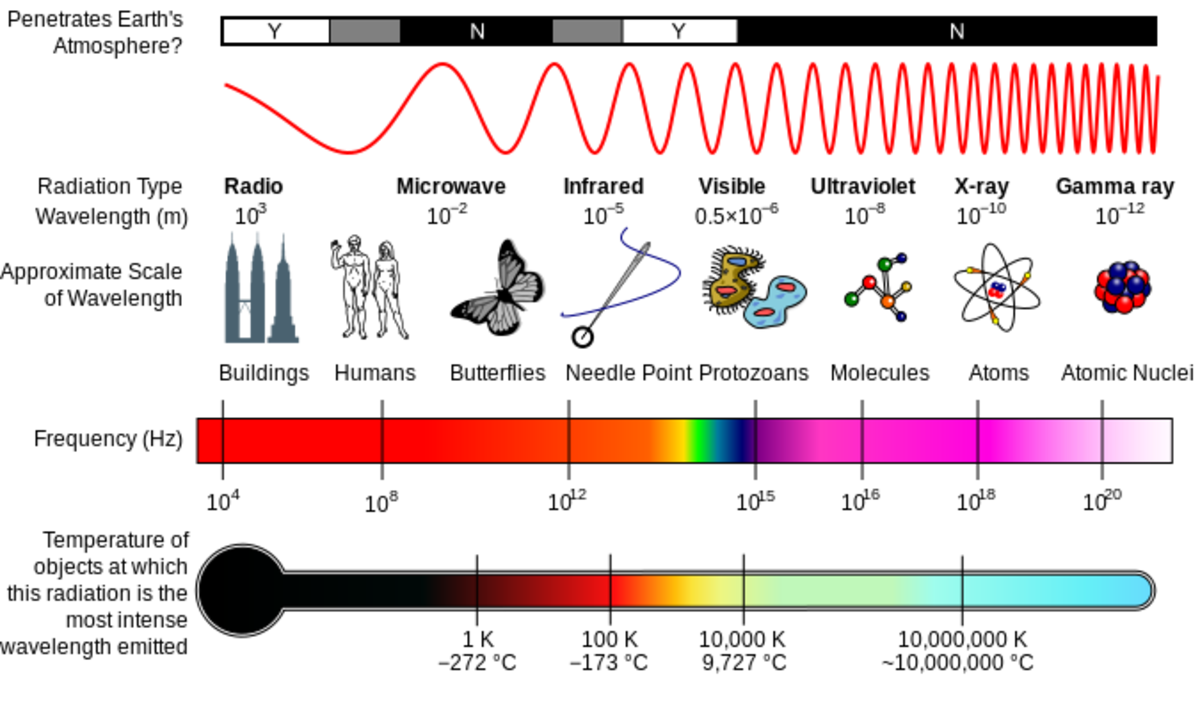
Microwave Radiation Drawing - 19 ghz from the roof of the physics building. Web electromagnetic spectrum provides clearly information of molecules if they are rotational transitions, vibrational transitions, or electronic transitions. Shorter wavelengths with higher frequencies make up the optical spectrum. Key takeaway understanding the electronic structure of atoms requires an understanding of the properties of waves and electromagnetic radiation. Web in this lab, we seek to recreate this founding pillar of modern physics. They fall between infrared radiation and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. Web updated on august 12, 2021 microwave radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation. Because the expanding universe has cooled since this primordial explosion, the background radiation is in the microwave region of the electromagnetic spectrum. Web in this review, recent approaches examining the effects of microwave radiations on the brain, specifically learning and memory capabilities, as well as the mechanisms of brain dysfunction with exposure as reported in the literature, are analyzed and interpreted to provide prospective views for future research directed at this important. Web beyond the red end of the visible range but at frequencies higher than those of radar waves and microwaves is the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, between frequencies of 10 12 and 5 × 10 14 hz (or wavelengths from 0.1 to 7.5 × 10 −5 cm). Using a digital keypad to set the microwave oven power level and microwaving time for cooking or reheating. Types of rays vector illustration. Alpha, beta, gamma, x rays, neutrons, neutrinos rays. Web list the following forms of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing wavelength: Web microwave rotational spectroscopy uses microwave radiation to measure the energies of rotational transitions for molecules. Web microwaves are defined as electromagnetic radiations with a frequency ranging between 300 mhz to 300 ghz. Web non ionizing and ionizing radiation. Web microwave rotational spectroscopy uses microwave radiation to measure the energies of rotational transitions for molecules in the gas phase. A molecule or a set of molecules can be read by the absorption of microwave radiation which. Currently, 2.45 ghz microwaves are primarily used for heating and sterilisation within the food industry and the thermal methods of this process are relatively well known. 19 ghz from the roof of the physics building. Web non ionizing and ionizing radiation. The wave model is useful for explaining many features of electromagnetic radiation, and the particle model explains other features.. Currently, 2.45 ghz microwaves are primarily used for heating and sterilisation within the food industry and the thermal methods of this process are relatively well known. List them in order of increasing frequency. Web microwave rotational spectroscopy uses microwave radiation to measure the energies of rotational transitions for molecules in the gas phase. Shorter wavelengths with higher frequencies make up. Web in this lab, we seek to recreate this founding pillar of modern physics. They fall between infrared radiation and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum. An rf signal is a signal that is coherently generated, radiated by a transmit antenna, propagated through air or space, collected by a receive antenna, and then amplified and information extracted. Web microwaves are. Web the cosmic microwave background radiation (cmbr) is microwave radiation that permeates all of space, and its discovery supports the big bang theory of the origin of the universe. Currently, 2.45 ghz microwaves are primarily used for heating and sterilisation within the food industry and the thermal methods of this process are relatively well known. A radiometer is used to. The wave model is useful for explaining many features of electromagnetic radiation, and the particle model explains other features. It accomplishes this through the interaction of the electric dipole moment of the molecules with the electromagnetic field of the exciting microwave photon. This is usually done to avoid describing the radiations as 'microwave' radiation. Web non ionizing and ionizing radiation.. Web non ionizing and ionizing radiation. Describe where microwaves are found on the ems compared to the other six forms of radiation. Currently, 2.45 ghz microwaves are primarily used for heating and sterilisation within the food industry and the thermal methods of this process are relatively well known. They fall between infrared radiation and radio waves in the electromagnetic spectrum.. It accomplishes this through the interaction of the electric dipole moment of the molecules with the electromagnetic field of the exciting microwave photon. I love microwaves, i think they are the coolest thing ever. Web microwaves are defined as electromagnetic radiations with a frequency ranging between 300 mhz to 300 ghz. Web microwave rotational spectroscopy uses microwave radiation to measure. In your description, compare and contrast its wavelength, frequency and energy with those of other regions of the ems. Shorter wavelengths with higher frequencies make up the optical spectrum. Web non ionizing and ionizing radiation. Alpha, beta, gamma, x rays, neutrons, neutrinos rays. This is usually done to avoid describing the radiations as 'microwave' radiation. Web the electromagnetic spectrum is comprised of all frequencies of electromagnetic radiation that propagate energy and travel through space in the form of waves. Shorter wavelengths with higher frequencies make up the optical spectrum. Longer wavelengths with lower frequencies make up the radio spectrum. It accomplishes this through the interaction of the electric dipole moment of the molecules with the electromagnetic field of the exciting microwave photon. Web electromagnetic radiation (e.g., radio, microwaves, light) can be modeled as a wave of changing electric and magnetic fields or as particles called photons. Microwaves are a versatile electromagnetic wave with a variety of uses within and beyond medicine ( table 1 ). The experiment consists of a temperature measurement of the cmb, which is actually “light” left over from the big bang. Web updated on august 12, 2021 microwave radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation. Web list the following forms of electromagnetic radiation in order of increasing wavelength: Web the cosmic microwave background radiation (cmbr) is microwave radiation that permeates all of space, and its discovery supports the big bang theory of the origin of the universe. In contrast, the wavelength ranges from 1 mm to around 30 cm. My science teacher even let me teach a lesson (that i made) on microwaves! A radiometer is used to measure the intensity of the sky signal at. Web beyond the red end of the visible range but at frequencies higher than those of radar waves and microwaves is the infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum, between frequencies of 10 12 and 5 × 10 14 hz (or wavelengths from 0.1 to 7.5 × 10 −5 cm). Cosmic microwave background (cmb), electromagnetic radiation filling the universe that is a residual effect of the big bang 13.8 billion years ago. In your description, compare and contrast its wavelength, frequency and energy with those of other regions of the ems.
Radiation and Microwave Techniques YouTube

Schematic drawing of the microwave radiation exposure system
What is Microwave Radiation? (with pictures)

How to Draw a Microwave HelloArtsy

Diagram describing the microwave radiation mechanism. The laser pulse

GEOSET Radiation in Your Kitchen Basic Microwave Oven Physics GEOSET
How to Draw a Microwave
Example Of Microwaves Spectrum

(a) Measured gain for microwave radiation from a rectangular horn with
Principle of Microwave Radio Communications TurboFuture
The Portion Of The Spectrum That We.
19 Ghz From The Roof Of The Physics Building.
Web In This Lab, We Seek To Recreate This Founding Pillar Of Modern Physics.
On This Instructable I Will Teach You A Thing Or Two About Microwave Radiation.
Related Post: