Occipital Bone Drawing
Occipital Bone Drawing - Image retrieved from anatomy standard. Web basics of drawing skulls when it comes to drawing skulls, there are a few things you need to keep in mind. It forms immobile and mobile joints, contains grooves that protect certain cranial nerves and blood vessels, and hosts a number of raised or flat surfaces onto which muscles and ligaments can attach. This article will describe the anatomy from the inferior view of the skull base. The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from anterolateral. Web the occipital bone is an unpaired bone which covers the back of the head (occiput). Bodytomy explains the anatomy, diagram, and function of the occipital bone. Consolidate your knowledge about the base of the skull with the following quiz! Web the occipital bone is the most posterior cranial bone and the main bone of the occiput. The scalp, which consists of five layers, covers the bone. On its outside surface, at the posterior midline, is a small protrusion called the external occipital protuberance, which serves as an attachment site for a ligament of the posterior neck. Inferior view of the base of the skull [23:24] structures seen on the inferior view of the base of the skull. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself. The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from anterior. It is considered a flat bone, like all other cranial bones, meaning that its primary function is either for protection or to provide a broad surface for muscle attachment. This article will describe the anatomy from the inferior view of the skull base. It is subdivided into the facial bones and. It is considered a flat bone, like all other cranial bones, meaning that its primary function is either for protection or to provide a broad surface for muscle attachment. Web gross anatomy the occipital bone is composed of four parts: Where is the occipital bone located. Web identify the bony openings of the skull is the skeletal structure of the. Web the occipital bone is the most posterior cranial bone and the main bone of the occiput. Bodytomy explains the anatomy, diagram, and function of the occipital bone. The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from anterolateral. The scalp, which consists of five layers, covers the bone. It has been improved and the format has been updated with more detailed. So don’t try to copy someone else’s skull drawing; Web basics of drawing skulls when it comes to drawing skulls, there are a few things you need to keep in mind. Image retrieved from anatomy standard. The scalp, which consists of five layers, covers the bone. It is trapezoidal in shape. It has been improved and the format has been updated with more detailed examples. This image shows the different sulci created by the venous sinuses that pass along the internal surface of the os occipitale. Inferior view of the base of the skull [23:24] structures seen on the inferior view of the base of the skull. So don’t try to. It is trapezoidal in shape and curved on itself like a shallow dish. Image retrieved from anatomy standard. The occipital is an unpaired, trapezoidal cranial bone covering the back of the head. Web the occipital bone curves on itself and is trapezoid in shape. Web the occipital bone is an unpaired bone which covers the back of the head (occiput). This article will describe the anatomy from the inferior view of the skull base. The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from anterolateral. It is the most posterior of all the cranial bones, forming the back of the head (occiput). The occipital is an unpaired, trapezoidal cranial bone covering the back of the head. Where is the occipital bone located. Where is the occipital bone located. External/internal surfaces basilar part (basiocciput): The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. Web basics of drawing skulls when it comes to drawing skulls, there are a few things you need to keep in mind. The sphenoid bone, petrous processes of the temporal bones, and the basilar part of the occipital bone. So don’t try to copy someone else’s skull drawing; It forms immobile and mobile joints, contains grooves that protect certain cranial nerves and blood vessels, and hosts a number of raised or flat surfaces onto which muscles and ligaments can attach. Web the occipital bone (/ ˌ ɒ k ˈ s ɪ p ɪ t əl /) is a cranial. It is subdivided into the facial bones and the cranium, or cranial vault ( figure 7.3.1 ). External/internal surfaces basilar part (basiocciput): It forms immobile and mobile joints, contains grooves that protect certain cranial nerves and blood vessels, and hosts a number of raised or flat surfaces onto which muscles and ligaments can attach. The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from anterior. The external surface of the squamous part features: The occipital bone is divided into four parts arranged around. Bodytomy explains the anatomy, diagram, and function of the occipital bone. Web gross anatomy the occipital bone is composed of four parts: The occipital bone overlies the occipital lobes of the cerebrum. The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from superior. Image retrieved from anatomy standard. The occipital bone (/ˌɒkˈsɪpɪtəl/) is a cranial dermal bone and the main bone of the occiput (back and lower part of the skull). The occipital bone (os occipitale) is shown from posterior. The curved bone resembles a shallow dish. Inferior view of the base of the skull [23:24] structures seen on the inferior view of the base of the skull. It is trapezoidal in shape.
Occipital Bone ClipArt ETC
Inner Surface of the Occipital Bone ClipArt ETC

A Nod To The Occipital Bone And Your Health Body Wisdom CranioSacral

Occipital Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
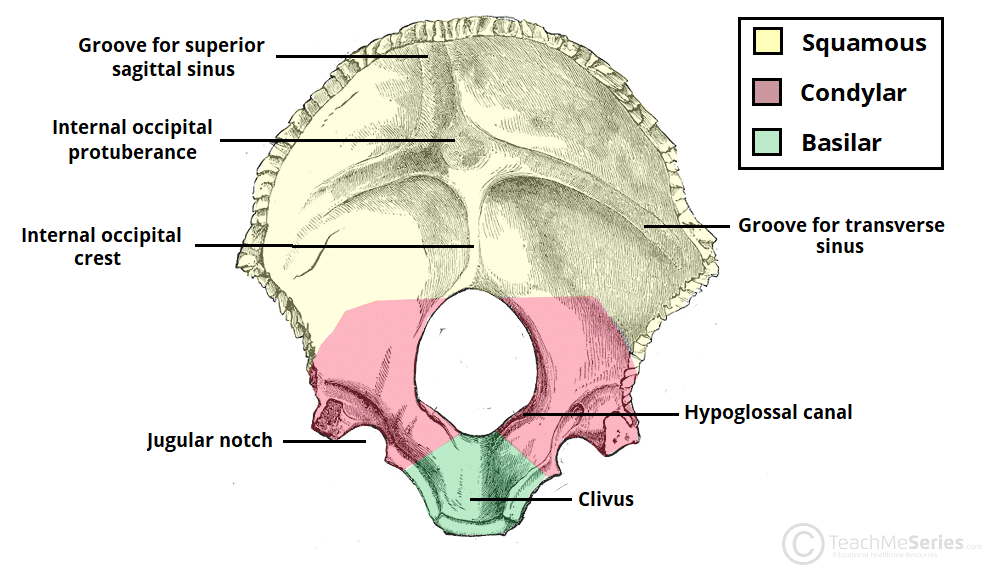
The Occipital Bone Landmarks Attachments TeachMeAnatomy

Occipital Bone The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
Human Anatomy Scientific Illustrations Occipital Bone Stock
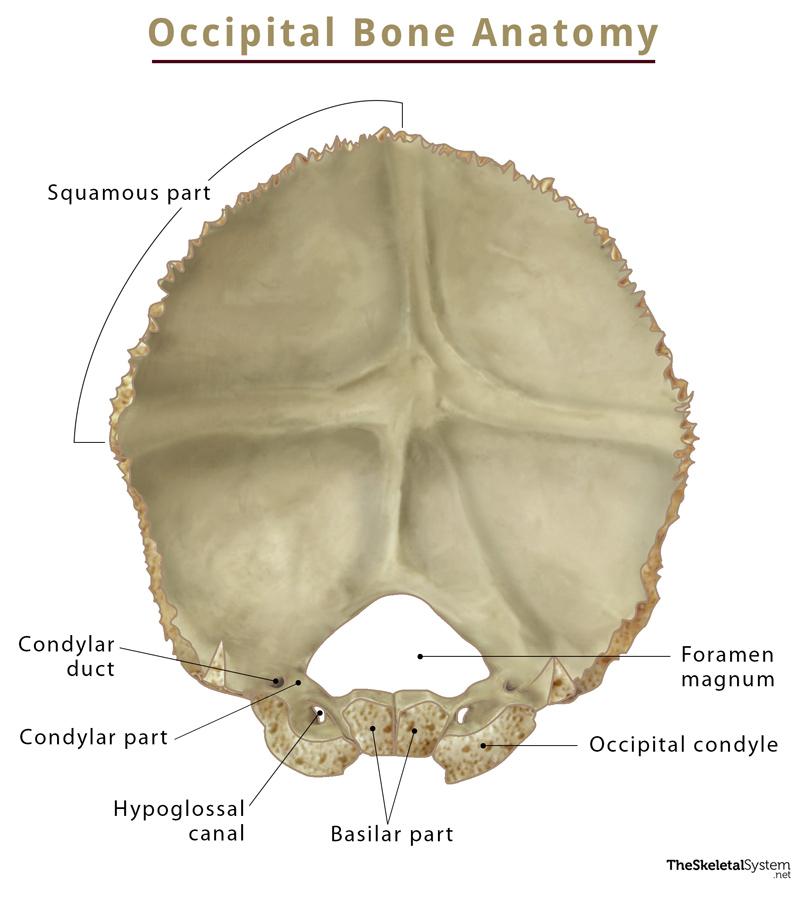
Occipital Bone Anatomy, Location, Functions, & Diagram

Occipital bone. Top view Anatomy bones, Occipital, Human anatomy
Internal Surface of the Occipital Bone ClipArt ETC
Web The Occipital Bone Curves On Itself And Is Trapezoid In Shape.
The Internal Surface Of The Squama (Eminentia Cruciformis, Cruciform Eminence) Is Caused By The Cerebellum And Cerebrum (Resp.
Web At The Base Of Skull In The Oc.
It Allows The Spinal Cord To Pass From The Brain Into The Spine.
Related Post:
