Ray Diagram Drawer
Ray Diagram Drawer - Pick one extreme on the image of the object and draw the reflected ray that will travel to the eye as the eye sights at this point. There are four steps to the construction of a ray diagram. Web this simulation shows a ray diagram for a concave mirror. Web first, we draw a dotted line from the tip of the object to the focal point on the opposite side. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. Then we draw a dotted line from the left focal point to the lens. A ray diagram must be drawn with a ruler, as all of the rays of light must be straight lines. The image formed by a single lens can be located and sized with three principal rays. Web in this keipert labs tutorial, we'll go through how to draw and construct a ray diagram. Web this demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. How does a lens or mirror form an image? Draw the image of the object. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. The method is applied to the task of drawing a ray diagram for an object located beyond the center of curvature (c) of a concave mirror. Web when pupils draw ray. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. Once through the lens, the ray. We'll go through the do's and don'ts and practice drawing diagrams f. Web this physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Which of the following diagrams shows the reflected ray correctly? This collection of interactive simulations allow learners of physics to explore core physics concepts by altering variables and observing the results. Web this demonstration lets you visualize the ray diagrams for converging and diverging lenses. Then we draw a dotted line from the left focal point to the lens. Web draw kinematic arrangement diagram and ray diagram for 6 speed. This is often from a source or object to an observer or screen. For implementing and testing how the formulae work. Observe how the image changes when you adjust the focal length of the lens, move the object, or move the screen. Web this physics video tutorial on optics provides a basic introduction into ray diagrams. Light rays are shown. By manipulating the object and lens locations, you can create real or virtual images. Also, an arrow on the tip of the ray shows the direction of propagation of light. Web a ray of light is incident on a spherical mirror at the pole, p. Which of the following diagrams shows the reflected ray correctly? The method is applied to. We'll go through the do's and don'ts and practice drawing diagrams f. Draw the incident ray for light traveling from the corresponding extreme on. Web the four steps of the process for drawing a ray diagram are listed, described and illustrated below. The method of drawing ray diagrams for a double concave lens is described below. Draw the image of. There are four steps to the construction of a ray diagram. Aperture should be smaller than radius of curvature 19. Next, we draw a ray parallel to the ground. Use the principle that the object distance is equal to the image distance to determine the exact location of the object. All rays are drawn with a ruler. Web eye to view the image of the object. This collection of interactive simulations allow learners of physics to explore core physics concepts by altering variables and observing the results. Using a straight edge, accurately draw one ray so that it passes exactly through the focal point on the way to the lens. But also, you can draw a ray. Draw the second ray such that it travels exactly parallel to the principal axis. The rays parallel to the principal axis and the ray through the center of. Web a ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. Source code is available on github. Draw the image of the. Web how do you draw a ray diagram? Light rays are shown in red, extensions. Draw the incident ray for light traveling from the corresponding extreme on. To show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. Draw a ray from the object to the lens that is parallel to the principal axis. Then we draw a ray traveling in the direction of the dotted line. Web a ray diagram is a representation of the possible paths light can take to get from one place to another. Web this simulation shows a ray diagram for a concave mirror. To show the refraction of a wave at a boundary. Web how do you draw a ray diagram? This collection of interactive simulations allow learners of physics to explore core physics concepts by altering variables and observing the results. Create & simulate 2d geometric optical scenes interactively. Which of the following diagrams shows the reflected ray correctly? Source code is available on github. Web steps to a concave lens ray diagram. We'll go through the do's and don'ts and practice drawing diagrams f. Examples are given for converging and diverging lenses and for the cases where the object is inside and outside the principal focal length. Aperture should be smaller than radius of curvature 19. How does a lens or mirror form an image? There are four steps to the construction of a ray diagram. When you draw ray diagrams on the board or on a transparency:Ray diagrams for convex mirrors

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
How to Draw Ray Diagram (POWERPOINT)
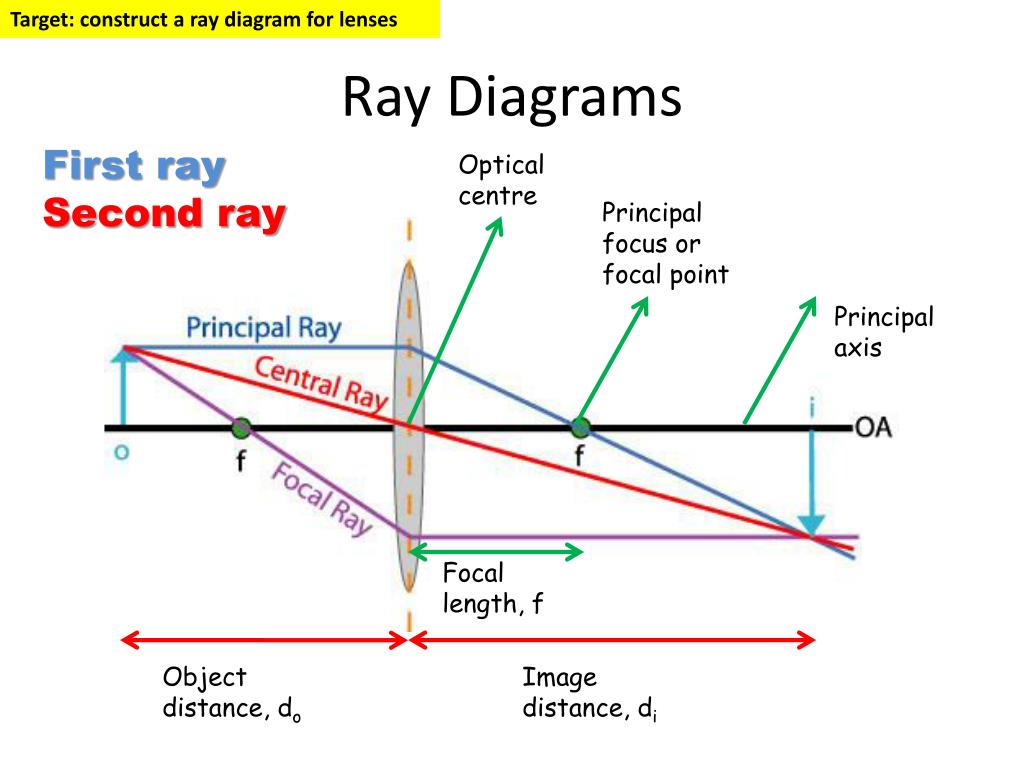
Draw A Labelled Ray Diagram For Image Formation By A Concave Mirror

Convex Mirror Ray diagram, Images Formed with Steps Teachoo
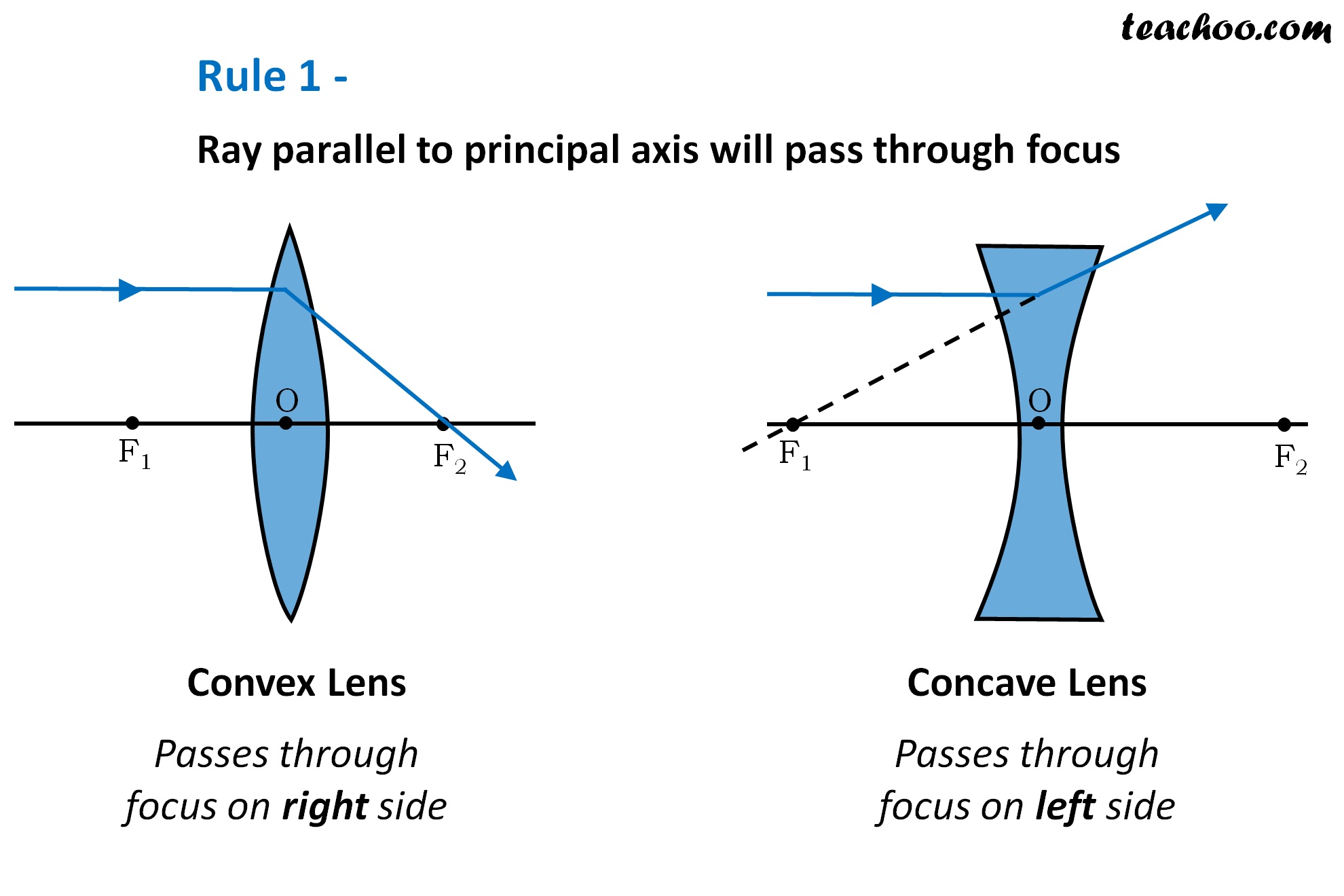
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Convex and Concave Lens Teachoo
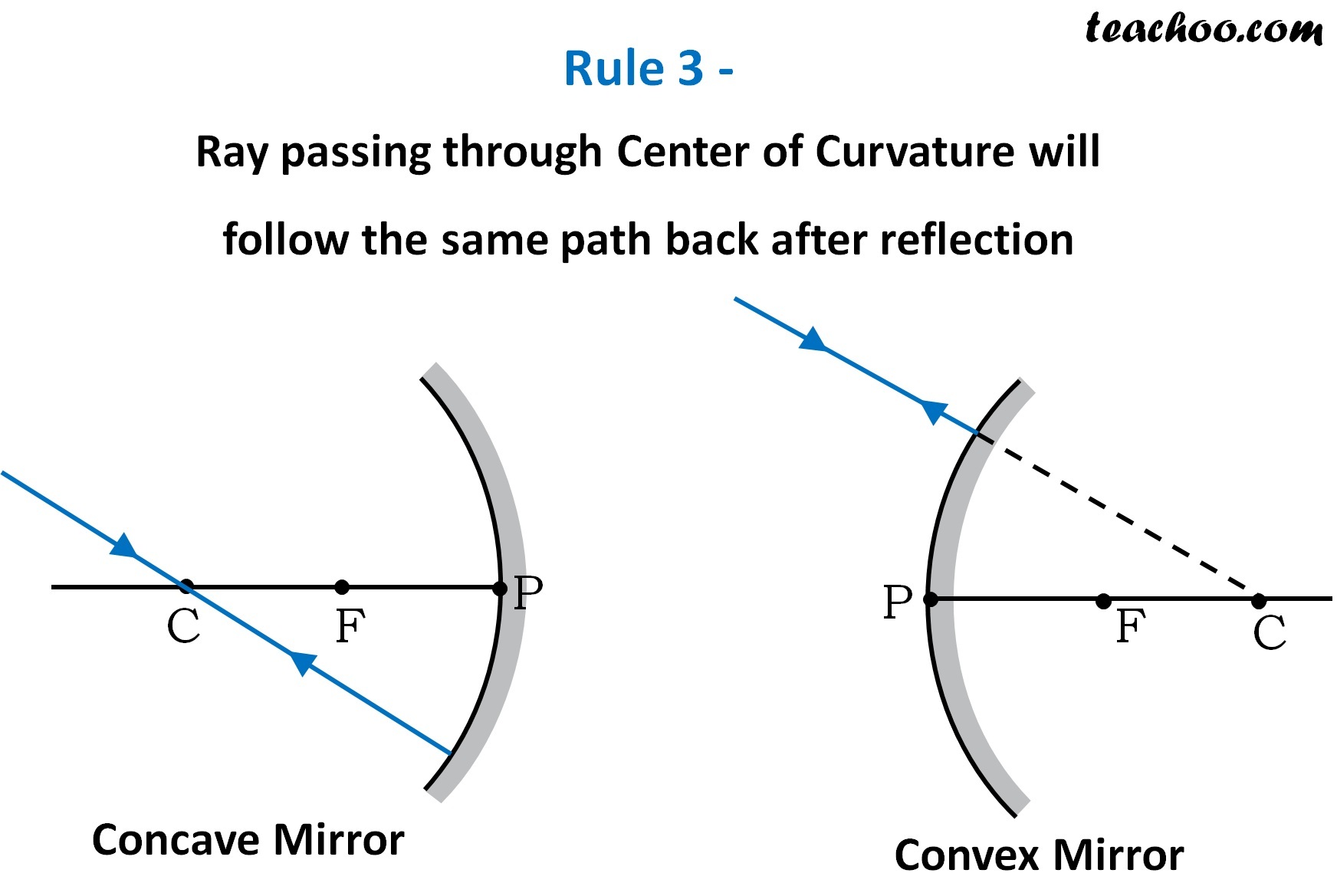
Rules for drawing Ray Diagram in Concave and Convex Mirror Teachoo

Draw a ray diagram for concave mirror when object

How to draw ray diagrams // Convex lens ray diagrams // Class 10
The Smooth Side Is The Reflecting Part Of The Mirror, And The Dotted Side Is The Back.
Light Travels In Straight Lines Within A Uniform Medium (This Means That Light Can Change Direction Upon Entering A Different Medium).
Pick A Point On The Top Of The Object And Draw Three Incident Rays Traveling Towards The Lens.
Web For Example, You Can Draw A Ray Of Light Parallel To The Principal Axis Which Reflects Off The Mirror And Passes Through The Principal Focus (Like In This Video).
Related Post:
.PNG)
