Draw And Label The Cell Cycle
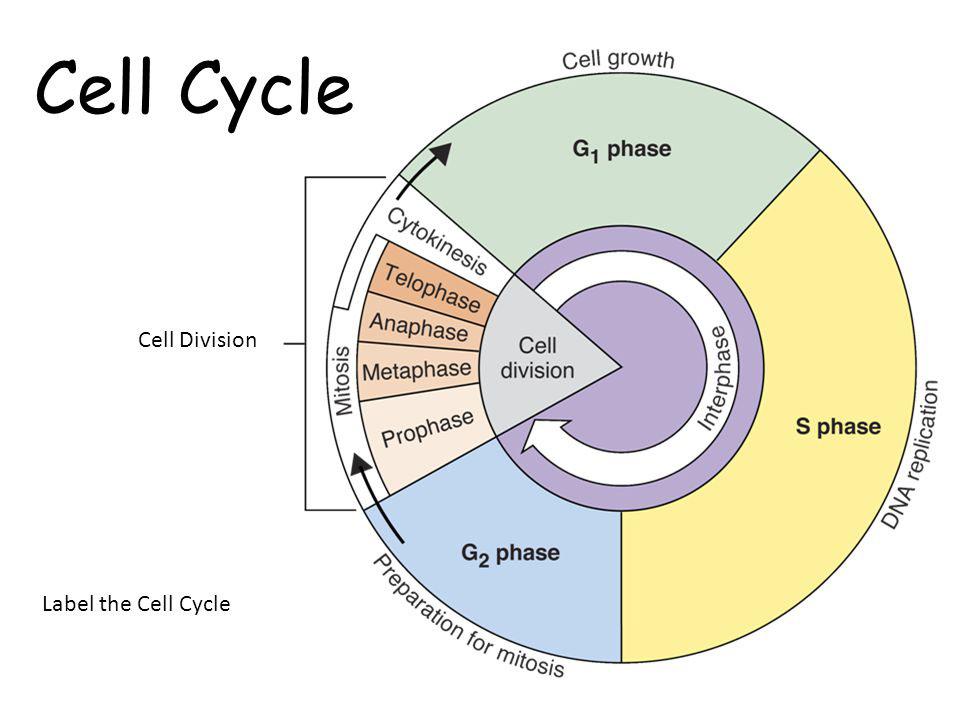
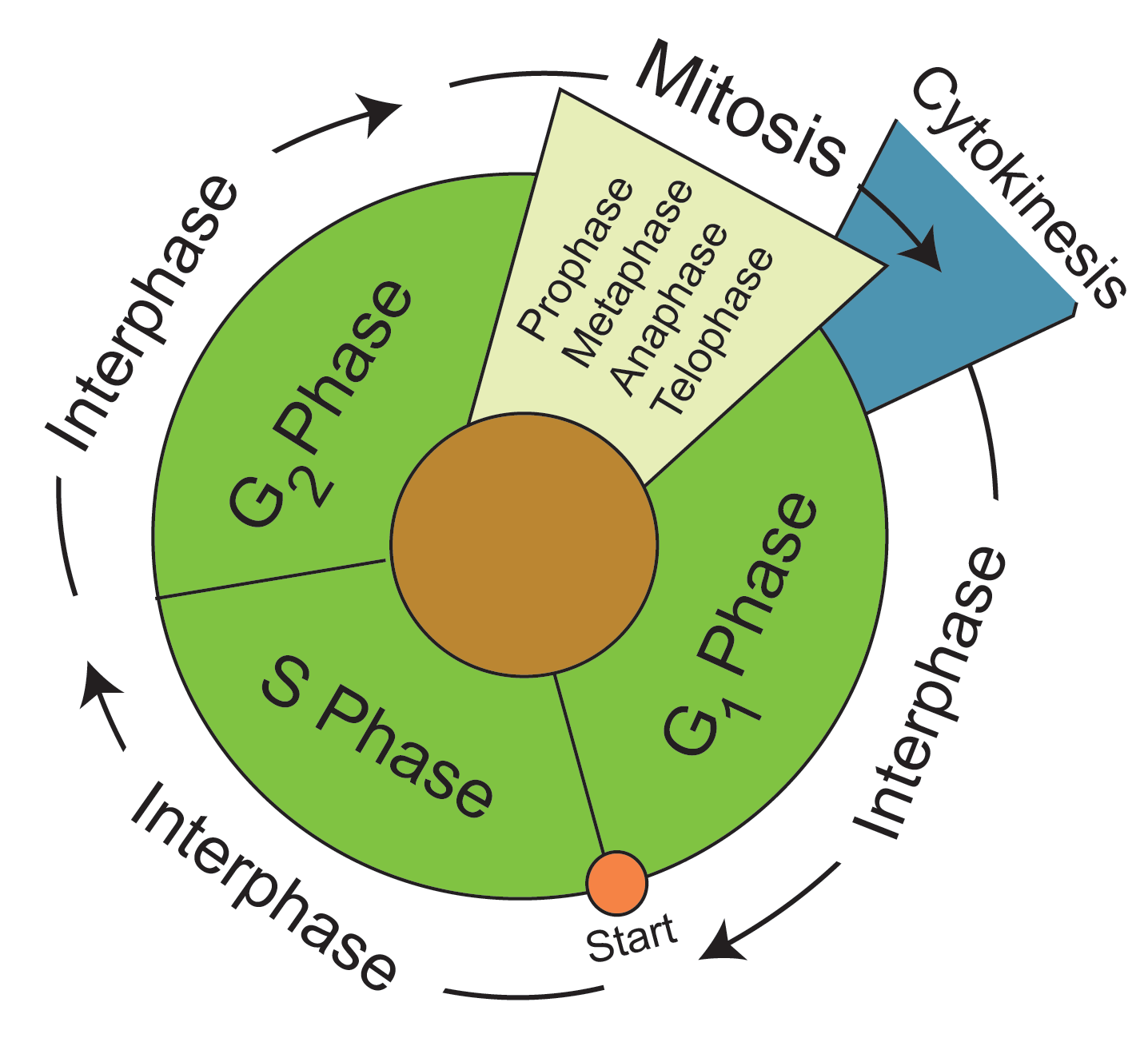
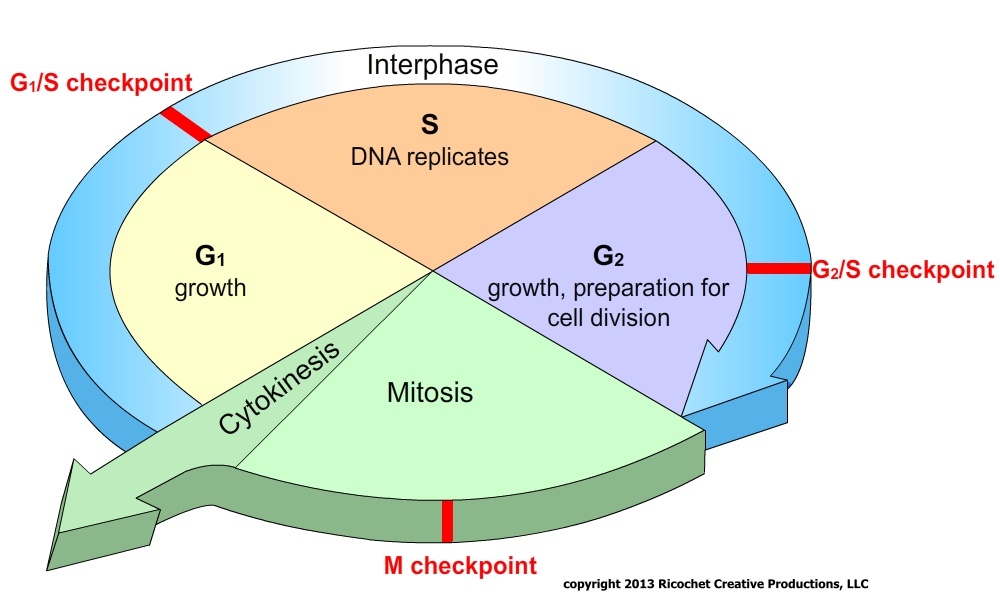
Draw And Label The Cell Cycle - In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. Web study with quizlet and memorize flashcards containing terms like describe the overall purposes of cell division and the cell cycle., draw the eukaryotic cell cycle, labeling the different phases and describing what occurs in each., describe the structure of eukaryotic chromosomes, drawing a labeled picture of a chromosome after s phase and more. G 2 (gap 2) phase 4. These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm. The stages g1, s, and g2 make up interphase, which accounts for the span between cell divisions. Compare your list to your classmates. Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. Other types of cells, however, can divide much more rapidly. Compare your list to your classmates. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. Human sperm and eggs, which have only one homologous chromosome from each pair, are. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. Other types of cells, however, can divide much. For a typical rapidly proliferating human cell with a total cycle time of 24 hours, the g 1 phase might last about 11 hours, s phase about 8 hours, g 2 about 4 hours, and m about 1 hour. Web locate the region of active cell division, known as the root apical meristem, which is about 1 mm behind the. What moves the chromatids during mitosis? The most basic function of the cell cycle is to duplicate accurately the vast amount of dna in the chromosomes and then segregate the copies precisely into two genetically identical daughter cells. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication,. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web locate the region of active cell division, known as the root apical meristem, which is about 1 mm behind the actual tip of the root. The main phases are shown: Labeling diagrams examine the images below. The. In other words, it is the series of growth and development steps a cell undergoes between its “birth”—formation by the division of a mother cell—and reproduction—division to make two new daughter cells. The role of mitosis in the cell cycle is to replicate the genetic material in an existing cell—known as the “parent cell”—and distribute that genetic material to two. Other types of cells, however, can divide much more rapidly. These processes define the two major phases of the cell cycle. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells.. When a sperm and an egg join in fertilization, the two haploid sets of chromosomes form a. Web the cell cycle is a cycle of stages that cells pass through to allow them to divide and produce new cells. G1 phase (first gap) s phase (synthesis of dna) g2 phase (second gap) mitosis. The g 1 phase is set in. Web an overview of the cell cycle. Web the 46 chromosomes of a human cell are organized into 23 pairs, and the two members of each pair are said to be homologues of one another (with the slight exception of the x and y chromosomes; Web the cell cycle can be thought of as the life cycle of a cell.. Web the cell cycle is an ordered series of events involving cell growth and cell division that produces two new daughter cells. Web the cell cycle can be thought of as the life cycle of a cell. Interphase is divided into g 1, s, and g 2 phases. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of. _____ during what phase does cytokinesis begin? Web to put that another way, meiosis in humans is a division process that takes us from a diploid cell—one with two sets of chromosomes—to haploid cells—ones with a single set of chromosomes. For a typical rapidly proliferating human cell with a total cycle time of 24 hours, the g 1 phase might last about 11 hours, s phase about 8 hours, g 2 about 4 hours, and m about 1 hour. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. Web the cell cycle is an orderly sequence of events. Mitosis is a type of cell division in which one cell (the mother) divides to produce two new cells (the daughters) that are genetically identical to itself. Cells on the path to cell division proceed through a series of precisely timed and carefully regulated stages of growth, dna replication, and division that produce two genetically identical cells. As completely as possible, list the key events that occur in each stage of mitosis. It is sometimes referred to as the “cell division cycle” for that reason. After completing the cycle it either starts the process again from g1 or exits through g0. Other types of cells, however, can divide much more rapidly. Mitosis is a process that occurs during the cell cycle. In other words, it is the series of growth and development steps a cell undergoes between its “birth”—formation by the division of a mother cell—and reproduction—division to make two new daughter cells. In eukaryotes, the cell cycle consists of a long preparatory period, called interphase. Web cell cycle or cell division refers to the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its maturity and subsequent division. These events include duplication of its genome and synthesis of the cell organelles followed by division of the cytoplasm.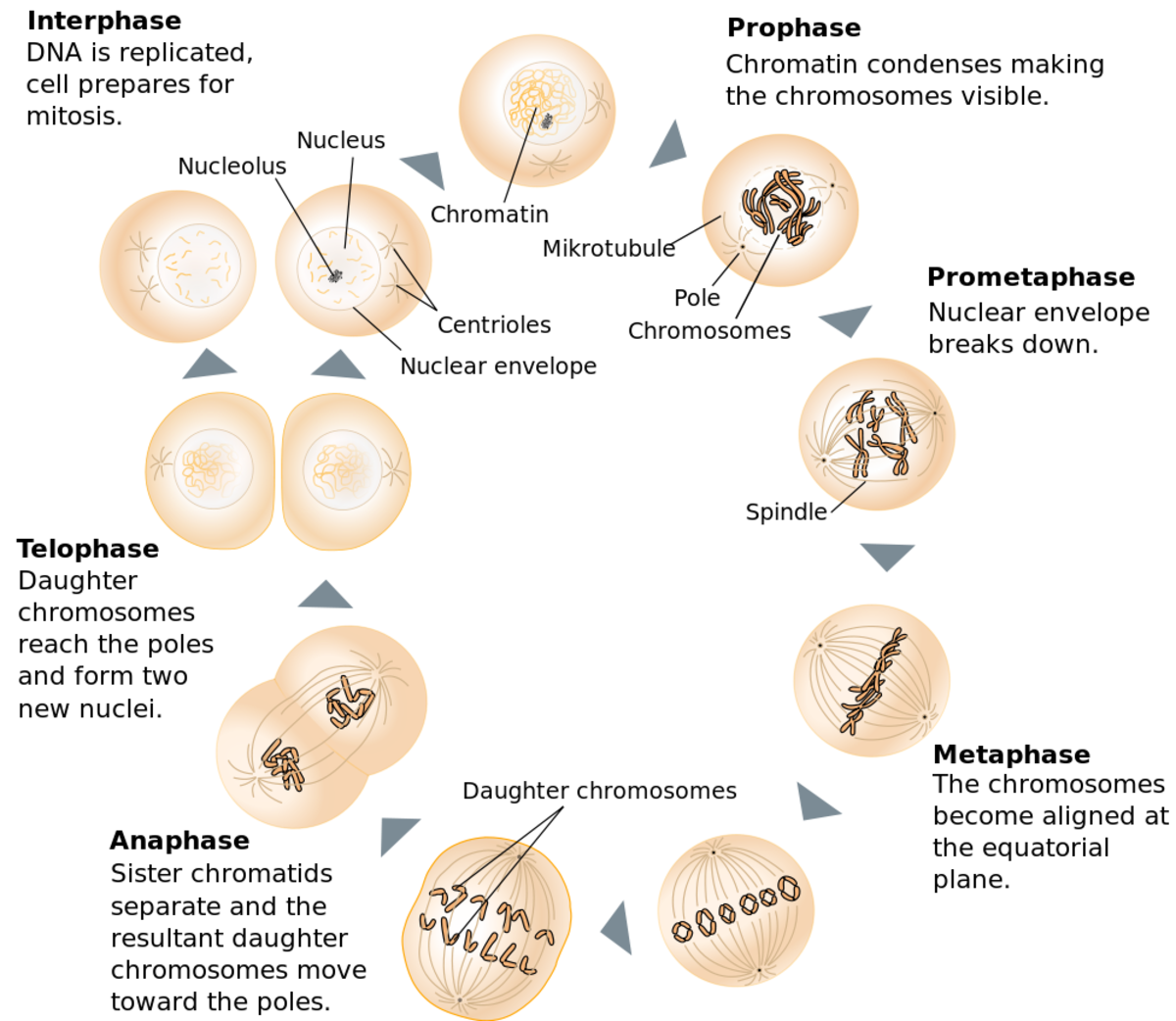
Cell Division Mitosis and Meiosis Owlcation
Phases of Cell cycle Online Biology Notes
Cell Cycle Phases , Diagram , Types and Comparison
Mrs.Cruz's Biology Class Chapter 5 Cell Growth and Division
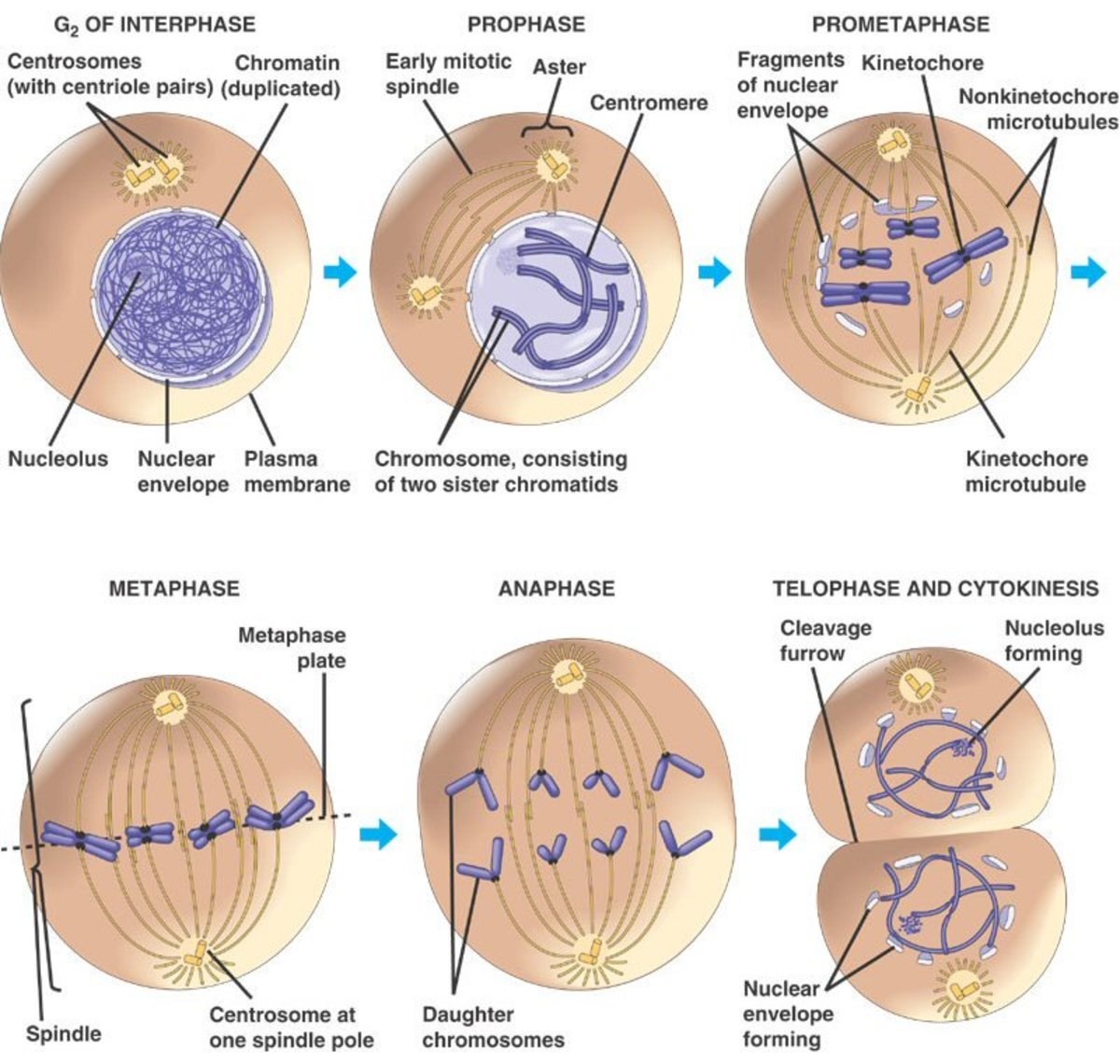
Stages of the Cell Cycle Mitosis (Metaphase, Anaphase and Telophase

Cell cycle labelling. Schematic representation of the cell cycle and

Cell Division An Intro AmoebaMike
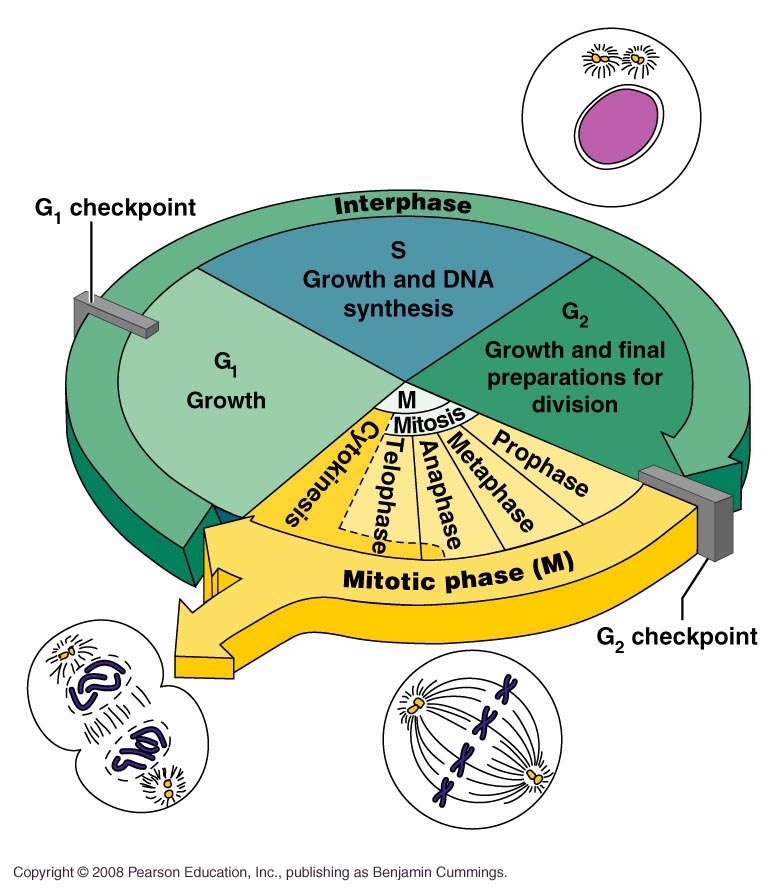
CSIR LIFE SCIENCE PREPARATION Fundamental Processes Overview of the

The Cell Cycle Phases Mitosis Regulation TeachMePhysiology

Cell Cycle Phase Definition, Fours phases of Cell cycle Division
_____ If A Human Cell Has 46 Chromosomes, How Many.
Web The Duration Of These Cell Cycle Phases Varies Considerably In Different Kinds Of Cells.
_____ What Anchors The Spindle?
Web The Cell Cycle.
Related Post: